Engineering of Cyclodextrin Glycosyltransferase through a Size/Polarity Guided Triple-Code Strategy with Enhanced α-Glycosyl Hesperidin Synthesis Ability
- PMID: 35950845
- PMCID: PMC9469708
- DOI: 10.1128/aem.01027-22
Engineering of Cyclodextrin Glycosyltransferase through a Size/Polarity Guided Triple-Code Strategy with Enhanced α-Glycosyl Hesperidin Synthesis Ability
Abstract
Hesperidin, a flavonoid enriched in citrus peel, can be enzymatically glycosylated using CGTase with significantly improved water solubility. However, the reaction catalyzed by wild-type CGTase is rather inefficient, reflected in the poor production rate and yield. By focusing on the aglycon attacking step, seven residues were selected for mutagenesis in order to improve the transglycosylation efficiency. Due to the lack of high-throughput screening technology regarding to the studied reaction, we developed a size/polarity guided triple-code strategy in order to reduce the library size. The selected residues were replaced by three rationally chosen amino acids with either changed size or polarity, leading to an extremely condensed library with only 32 mutants to be screened. Twenty-five percent of the constructed mutants were proved to be positive, suggesting the high quality of the constructed library. Specific transglycosylation activity of the best mutant Y217F was assayed to be 935.7 U/g, and its kcat/KmA is 6.43 times greater than that of the wild type. Homology modeling and docking computation suggest the source of notably enhanced catalytic efficiency is resulted from the combination of ligand transfer and binding effect. IMPORTANCE Size/polarity guided triple-code strategy, a novel semirational mutagenesis strategy, was developed in this study and employed to engineer the aglycon attacking site of CGTase. Screening pressure was set as improved hesperidin glucoside synthesis ability, and eight positive mutants were obtained by screening only 32 mutants. The high quality of the designed library confirms the effectiveness of the developed strategy is potentially valuable to future mutagenesis studies. Mechanisms of positive effect were explained. The best mutant exhibits 6.43 times enhanced kcat/KmA value and confirmed to be a superior whole-cell catalyst with potential application value in synthesizing hesperidin glucosides.
Keywords: cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase; hesperidin; mutagenesis strategy; transglycosylation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

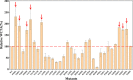


 ) and wild-type (blue circle,
) and wild-type (blue circle,  ). GH: hesperidin glucoside, G2H: hesperidin maltoside, G3H: hesperidin maltotrioside.
). GH: hesperidin glucoside, G2H: hesperidin maltoside, G3H: hesperidin maltotrioside.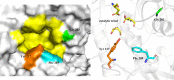
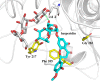
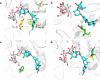

References
-
- Uitdehaag JC, van der Veen BA, Dijkhuizen L, Dijkstra BW. 2002. Catalytic mechanism and product specificity of cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase, a prototypical transglycosylase from the α-amylase family. Enzyme Microb Technol 30:295–304. 10.1016/S0141-0229(01)00498-7. - DOI
-
- Uitdehaag JC, Van Alebeek GJW, van der Veen BA, Dijkhuizen L, Dijkstra BW. 2000. Structures of maltohexaose and maltoheptaose bound at the donor sites of cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase give insight into the mechanisms of transglycosylation activity and cyclodextrin size specificity. Biochemistry 39:7772–7780. 10.1021/bi000340x. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

