Dominant Negative Mutants of Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Viral Infectivity Factor (Vif) Disrupt Core-Binding Factor Beta-Vif Interaction
- PMID: 35950859
- PMCID: PMC9472641
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.00555-22
Dominant Negative Mutants of Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Viral Infectivity Factor (Vif) Disrupt Core-Binding Factor Beta-Vif Interaction
Abstract
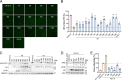
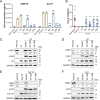
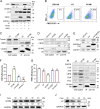
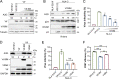
Apolipoprotein B mRNA-editing catalytic polypeptide-like 3 family members (APOBEC3s) are host restriction factors that inhibit viral replication. Viral infectivity factor (Vif), a human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) accessory protein, mediates the degradation of APOBEC3s by forming the Vif-E3 complex, in which core-binding factor beta (CBFβ) is an essential molecular chaperone. Here, we screened nonfunctional Vif mutants with high affinity for CBFβ to inhibit HIV-1 in a dominant negative manner. We applied the yeast surface display technology to express Vif random mutant libraries, and mutants showing high CBFβ affinity were screened using flow cytometry. Most of the screened Vif mutants containing random mutations of different frequencies were able to rescue APOBEC3G (A3G). In the subsequent screening, three of the mutants restricted HIV-1, recovered G-to-A hypermutation, and rescued APOBEC3s. Among them, Vif-6M showed a cross-protection effect toward APOBEC3C, APOBEC3F, and African green monkey A3G. Stable expression of Vif-6M in T lymphocytes inhibited the viral replication in newly HIV-1-infected cells and the chronically infected cell line H9/HXB2. Furthermore, the expression of Vif-6M provided a survival advantage to T lymphocytes infected with HIV-1. These results suggest that dominant negative Vif mutants acting on the Vif-CBFβ target potently restrict HIV-1. IMPORTANCE Antiviral therapy cannot eliminate HIV and exhibits disadvantages such as drug resistance and toxicity. Therefore, novel strategies for inhibiting viral replication in patients with HIV are urgently needed. APOBEC3s in host cells are able to inhibit viral replication but are antagonized by HIV-1 Vif-mediated degradation. Therefore, we screened nonfunctional Vif mutants with high affinity for CBFβ to compete with the wild-type Vif (wtVif) as a potential strategy to assist with HIV-1 treatment. Most screened mutants rescued the expression of A3G in the presence of wtVif, especially Vif-6M, which could protect various APOBEC3s and improve the incorporation of A3G into HIV-1 particles. Transduction of Vif-6M into T lymphocytes inhibited the replication of the newly infected virus and the chronically infected virus. These data suggest that Vif mutants targeting the Vif-CBFβ interaction may be promising in the development of a new AIDS therapeutic strategy.
Keywords: apolipoprotein B mRNA-editing catalytic polypeptide-like 3 family member (APOBEC3); core-binding factor beta (CBFβ); dominant negative mutant; human immunodeficiency virus (HIV); viral infectivity factor (Vif).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

