Dosages of Swallowing Exercises Prescribed in Stroke Rehabilitation: A Medical Record Audit
- PMID: 35951119
- PMCID: PMC10006267
- DOI: 10.1007/s00455-022-10500-x
Dosages of Swallowing Exercises Prescribed in Stroke Rehabilitation: A Medical Record Audit
Abstract
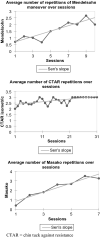
This study investigated how swallowing exercise dosage is recorded, and what swallowing exercise dosages are reported in a stroke rehabilitation setting. We additionally explored the relation between mean daily swallowing repetitions and likelihood of improvement in functional swallowing status and considered how swallowing exercise dosages in practice compared to evidence-based principles of neural plasticity and strength training. We audited medical records for 42 patients with post-stroke dysphagia admitted to an inpatient rehabilitation unit over 18 months. Data were collected on participant characteristics, swallowing exercises and dosages, and clinical outcomes. The relation between dosage and outcomes was investigated using logistic regression analysis. On average, patients were seen for a median of 2.4 swallowing intervention sessions per week (IQR: 1.7) over 21 days (IQR: 16) and received a median 44.5 swallowing exercise repetitions per session (IQR: 39.6). Results indicated variable reporting of swallowing exercise dosages. Frequency, intervention duration, exercise type, and number of repetitions were routinely recorded in medical records, while intensity, session length, content, and adherence to home exercise programs were not. Frequency of swallowing intervention was lower in practice compared to research studies, and swallowing exercises did not follow specificity or progressive resistance principles. Likelihood of improvement in swallowing status was partially explained by age (B = -.015, p = .007) but not by mean daily swallowing exercise repetitions. This study illustrates dosages of swallowing exercises used in clinical practice. Results highlight the need for improved consideration and reporting of dosage, and application of evidence-based principles to swallowing exercise dosages.
Keywords: Dose; Dysphagia; Exercise; Intervention; Medical Records; Stroke.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
"One of the biggest grey areas": A focus group study exploring dosage of swallowing exercises from speech-language pathologist perspectives.Int J Speech Lang Pathol. 2024 Jun;26(3):445-456. doi: 10.1080/17549507.2023.2240038. Epub 2023 Aug 31. Int J Speech Lang Pathol. 2024. PMID: 37652163
-
Chair-stand exercise improves post-stroke dysphagia.Geriatr Gerontol Int. 2020 Oct;20(10):885-891. doi: 10.1111/ggi.13998. Epub 2020 Aug 9. Geriatr Gerontol Int. 2020. PMID: 32772455
-
Adherence to preventive swallowing exercises for head and neck cancer patients undergoing (chemo)radiotherapy treatment.Acta Oncol. 2019 May;58(5):658-664. doi: 10.1080/0284186X.2018.1563715. Epub 2019 Jan 30. Acta Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30698049 Clinical Trial.
-
The use and effects of whole-body exercises on swallowing function: A scoping review.Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2023 Jul-Aug;58(4):1357-1374. doi: 10.1111/1460-6984.12858. Epub 2023 Feb 9. Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2023. PMID: 36759960
-
Efficacy of exercises to rehabilitate dysphagia: A critique of the literature.Int J Speech Lang Pathol. 2015 Jun;17(3):222-9. doi: 10.3109/17549507.2015.1024171. Epub 2015 Mar 31. Int J Speech Lang Pathol. 2015. PMID: 25825989 Review.
Cited by
-
Research hotspots and trends in post-stroke dysphagia: a bibliometric analysis.Front Neurosci. 2023 Oct 24;17:1275748. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1275748. eCollection 2023. Front Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37942140 Free PMC article.
-
Dosages of swallowing exercises in stroke rehabilitation: a systematic review.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2023 Mar;280(3):1017-1045. doi: 10.1007/s00405-022-07735-7. Epub 2022 Dec 6. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2023. PMID: 36471047 Free PMC article.
-
Positive relief of stroke patients with dysphagia under cluster nursing strategy.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Jan 26;103(4):e36143. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000036143. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 38277564 Free PMC article.
-
The application of cluster nursing to prevent bacterial pneumonia in stroke patients in neurology department.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Dec 29;102(52):e36657. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000036657. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 38206722 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Garber CE, Blissmer B, Deschenes MR, Franklin BA, Lamonte MJ, Lee I-M, Nieman DC, Swain DP. American College of Sports Medicine position stand: quantity and quality of exercise for developing and maintaining cardiorespiratory, musculoskeletal, and neuromotor fitness in apparently healthy adults: guidance for prescribing exercise. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2011;43(7):1334–1359. doi: 10.1249/MSS.0b013e318213fefb. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Pescatello LS, Riebe D, Thompson PD. ACSM's guidelines for exercise testing and prescription. United Kingdom: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2014. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical