The estimated disease burden of acute COVID-19 in the Netherlands in 2020, in disability-adjusted life-years
- PMID: 35951278
- PMCID: PMC9366822
- DOI: 10.1007/s10654-022-00895-0
The estimated disease burden of acute COVID-19 in the Netherlands in 2020, in disability-adjusted life-years
Abstract
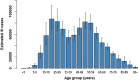
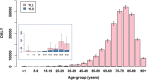
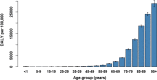
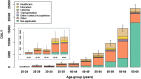
The impact of COVID-19 on population health is recognised as being substantial, yet few studies have attempted to quantify to what extent infection causes mild or moderate symptoms only, requires hospital and/or ICU admission, results in prolonged and chronic illness, or leads to premature death. We aimed to quantify the total disease burden of acute COVID-19 in the Netherlands in 2020 using the disability-adjusted life-years (DALY) measure, and to investigate how burden varies between age-groups and occupations. Using standard methods and diverse data sources (mandatory notifications, population-level seroprevalence, hospital and ICU admissions, registered COVID-19 deaths, and the literature), we estimated years of life lost (YLL), years lived with disability, DALY and DALY per 100,000 population due to COVID-19, excluding post-acute sequelae, stratified by 5-year age-group and occupation category. The total disease burden due to acute COVID-19 was 286,100 (95% CI: 281,700-290,500) DALY, and the per-capita burden was 1640 (95% CI: 1620-1670) DALY/100,000, of which 99.4% consisted of YLL. The per-capita burden increased steeply with age, starting from 60 to 64 years, with relatively little burden estimated for persons under 50 years old. SARS-CoV-2 infection and associated premature mortality was responsible for a considerable direct health burden in the Netherlands, despite extensive public health measures. DALY were much higher than for other high-burden infectious diseases, but lower than estimated for coronary heart disease. These findings are valuable for informing public health decision-makers regarding the expected COVID-19 health burden among population subgroups, and the possible gains from targeted preventative interventions.
Keywords: COVID-19; Disability-adjusted life-years; Disease burden; Netherlands; Pandemic.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Coronavirus dashboard: current situation in the Netherlands. https://coronadashboard.government.nl/n. Accessed 30 June 2021.
-
- Statistics Netherlands. Ten thousand COVID-19 deaths during first wave of the pandemic. CBS; 1 October 2020. Available from: https://www.cbs.nl/en-gb/news/2020/40/10-thousand-covid-19-deaths-during...
-
- Statistics Netherlands. Deaths; cause of death (extensive list), age and sex. CBS; 11 January 2022. Available from: https://opendata.cbs.nl/statline/#/CBS/en/dataset/7233ENG/table?ts=16463...
-
- Lagerweij G, et al. Staat van Infectieziekten in Nederland, 2019 [The state of infectious diseases in the Netherlands, 2019]. Bilthoven: RIVM, 2021.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

