International consensus recommendations for management of New Onset Refractory Status Epilepticus (NORSE) including Febrile Infection-Related Epilepsy Syndrome (FIRES): Summary and Clinical Tools
- PMID: 35951466
- PMCID: PMC9826478
- DOI: 10.1111/epi.17391
International consensus recommendations for management of New Onset Refractory Status Epilepticus (NORSE) including Febrile Infection-Related Epilepsy Syndrome (FIRES): Summary and Clinical Tools
Abstract
Objective: To develop consensus-based recommendations for the management of adult and pediatric patients with NORSE/FIRES based on best available evidence and expert opinion.
Methods: The Delphi methodology was followed. A facilitator group of 9 experts was established, who defined the scope, users and suggestions for recommendations. Following a review of the current literature, recommendation statements concerning diagnosis, treatment and research directions were generated which were then voted on a scale of 1 (strongly disagree) to 9 (strongly agree) by a panel of 48 experts in the field. Consensus that a statement was appropriate was reached if the median score was greater than or equal to 7, and inappropriate if the median score was less than or equal to 3.
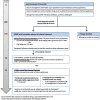
Results: Overall, 85 recommendation statements achieved consensus. The recommendations are divided into five sections: 1) disease characteristics, 2) diagnostic testing and sampling, 3) acute treatment, 4) treatment in the post-acute phase, and 5) research, registries and future directions in NORSE/FIRES. These are summarized in this article along with two practical clinical flowsheets: one for diagnosis and evaluation and one for acute treatment. A corresponding evidence-based analysis of all 85 recommendations alongside responses by the Delphi panel is presented in a companion article.
Significance: The recommendations generated by this consensus can be used as a guide for the diagnosis, evaluation, and management of patients with NORSE/FIRES, and for planning of future research.
Keywords: Adult; Anti-seizure medication; Delphi; Epilepsy; Immunotherapy; Ketogenic diet; Pediatric; Refractory status epilepticus; Status epilepticus.
This article is protected by copyright. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
RW has served on scientific advisory boards for GW Pharma and Octapharma and has received speaker honoraria from Eisai and Sanofi. OT was supported by research grant from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) (P20GM130447). RD has received speaker honorarium fee from Sobi. ETP has received a speaker honorarium from Eisai. RN has no disclosures for this study. SK has served on scientific advisory boards for Zogenix and Neurelis. NG has no disclosures for this study. LJH has received consultation fees for advising from Accure, Aquestive, Ceribell, Eisai, Marinus, Medtronic, Neurelis, Neuropace, and UCB; royalties from Wolters‐Kluwer for authoring chapters for UpToDate‐Neurology and from Wiley for co‐authoring the book “Atlas of EEG in Critical Care,” by Hirsch and Brenner; and honoraria for speaking from Neuropace, Natus, and UCB. NS has served on scientific advisory boards for GW Pharma, BioMarin, Arvelle, Marinus, and Takeda; has received speaker honoraria from Eisai, Biomarin, Livanova, and Sanofi; and has served as an investigator for Zogenix, Marinus, Biomarin, UCB, and Roche. RW, OT, RN, SK, NG, and LJH are members of the Scientific Board of the NORSE Institute. The present study is not industry sponsored. We confirm that we have read the Journal's position on issues involved in ethical publication and affirm that this report is consistent with those guidelines.
Figures

References
-
- Hirsch LJ, Gaspard N, van Baalen A, Nabbout R, Demeret S, Loddenkemper T, et al. Proposed consensus definitions for new‐onset refractory status epilepticus (NORSE), febrile infection‐related epilepsy syndrome (FIRES), and related conditions. Epilepsia. 2018;59:739–44. - PubMed
-
- Kortvelyessy P, Lerche H, Weber Y. FIRES and NORSE are distinct entities. Epilepsia. 2012;53:1276. - PubMed
-
- Gaspard N, Hirsch LJ, Sculier C, Loddenkemper T, van Baalen A, Lancrenon J, et al. New‐onset refractory status epilepticus (NORSE) and febrile infection‐related epilepsy syndrome (FIRES): state of the art and perspectives. Epilepsia. 2018;59:745–52. - PubMed
-
- Sculier C, Gaspard N. New onset refractory status epilepticus (NORSE). Seizure. 2019;68:72–8. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

