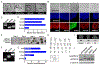
Derivation of spinocerebellar ataxia type 3 human embryonic stem cell line UMICHe001-A/UM134-1
- PMID: 35952620
- PMCID: PMC10020865
- DOI: 10.1016/j.scr.2022.102873
Derivation of spinocerebellar ataxia type 3 human embryonic stem cell line UMICHe001-A/UM134-1
Abstract
The most common autosomal dominant ataxia worldwide, spinocerebellar ataxia type 3 (SCA3) is a fatal, progressive neurodegenerative disorder caused by a CAG trinucleotide repeat expansion in the ATXN3 gene. Here we report the generation of human embryonic stem cell (hESC) line UM134-1, the first SCA3 disease-specific hESC line to be added to the NIH hESC registry. UM134-1 pluripotency was confirmed by immunocytochemistry and PCR for pluripotency markers and by the ability to form three germ layers in vitro. The established hESC line provides a useful new human cell model to study the pathogenesis of SCA3.
Copyright © 2022. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Moore LR, Keller L, Bushart DD, Delatorre RG, Li D, McLoughlin HS, do Carmo Costa M, Shakkottai VG, Smith GD, Paulson HL, 2019. Antisense oligonucleotide therapy rescues aggresome formation in a novel spinocerebellar ataxia type 3 human embryonic stem cell line. Stem Cell Res. 39, 101504. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials