Epigenetic reader SP140 loss of function drives Crohn's disease due to uncontrolled macrophage topoisomerases
- PMID: 35952671
- PMCID: PMC9442451
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2022.06.048
Epigenetic reader SP140 loss of function drives Crohn's disease due to uncontrolled macrophage topoisomerases
Abstract
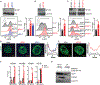
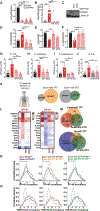
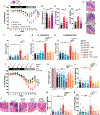
How mis-regulated chromatin directly impacts human immune disorders is poorly understood. Speckled Protein 140 (SP140) is an immune-restricted PHD and bromodomain-containing epigenetic "reader," and SP140 loss-of-function mutations associate with Crohn's disease (CD), multiple sclerosis (MS), and chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). However, the relevance of these mutations and mechanisms underlying SP140-driven pathogenicity remains unexplored. Using a global proteomic strategy, we identified SP140 as a repressor of topoisomerases (TOPs) that maintains heterochromatin and macrophage fate. In humans and mice, SP140 loss resulted in unleashed TOP activity, de-repression of developmentally silenced genes, and ultimately defective microbe-inducible macrophage transcriptional programs and bacterial killing that drive intestinal pathology. Pharmacological inhibition of TOP1/2 rescued these defects. Furthermore, exacerbated colitis was restored with TOP1/2 inhibitors in Sp140-/- mice, but not wild-type mice, in vivo. Collectively, we identify SP140 as a TOP repressor and reveal repurposing of TOP inhibition to reverse immune diseases driven by SP140 loss.
Keywords: Crohn’s disease; PHD; SP140; Speckled Protein; bromodomain; chromatin; epigenetic reader; inflammatory bowel disease; macrophages; topoisomerase.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests K.L.J. and H.A. are employees and shareholders of Moderna Inc., 200 Technology Square, Cambridge, MA 02138, since November 2021 and May 2022, respectively, after the time that this research was conducted. K.L.J. is a member of the scientific advisory board for Ancilia Biosciences. None of these relationships influenced the work in this study.
Figures



References
-
- Abramson J, Giraud M, Benoist C, and Mathis D (2010). Aire’s partners in the molecular control of immunological tolerance. Cell 140, 123–135. - PubMed
-
- Andersen FF, Tange TØ, Sinnathamby T, Olesen JR, Andersen KE, Westergaard O, Kjems J, and Knudsen BR (2002). The RNA splicing factor ASF/SF2 inhibits human topoisomerase I mediated DNA relaxation. J. Mol. Biol 322, 677–686. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

