His-163 is a stereospecific proton donor in the mechanism of d-glucosaminate-6-phosphate ammonia-lyase
- PMID: 35953460
- PMCID: PMC9529869
- DOI: 10.1002/1873-3468.14469
His-163 is a stereospecific proton donor in the mechanism of d-glucosaminate-6-phosphate ammonia-lyase
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: His-163 is a stereospecific proton donor in the mechanism of d-glucosaminate-6-phosphate ammonia-lyase.FEBS Lett. 2022 Dec;596(23):3103. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.14517. Epub 2022 Oct 25. FEBS Lett. 2022. PMID: 36281965 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
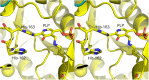
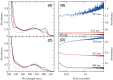
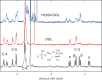
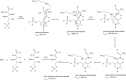
d-Glucosaminate-6-phosphate ammonia-lyase (DGL) catalyzes the conversion of d-glucosaminate-6-phosphate to 2-keto-3-deoxyglutarate-6-phosphate, with stereospecific protonation of C-3 of the product. The crystal structure of DGL showed that His-163 could serve as the proton donor. H163A mutant DGL is fully active in the steady-state reaction, and the pre-steady-state kinetics are very similar to those of wild-type DGL. However, H163A DGL accumulates a transient intermediate with λmax at 293 nm during the reaction that is not seen with wild-type DGL. Furthermore, NMR analysis of the reaction of H163A DGL in D2 O shows that the product is a mixture of deuterated diastereomers at C-3. These results establish that His-163 is the proton donor in the reaction mechanism of DGL.
Keywords: aminoacrylate intermediate; elimination reaction; pyridoxal-5′-phosphate; stereochemistry.
© 2022 The Authors. FEBS Letters published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Federation of European Biochemical Societies.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Structure and Mechanism of d-Glucosaminate-6-phosphate Ammonia-lyase: A Novel Octameric Assembly for a Pyridoxal 5'-Phosphate-Dependent Enzyme, and Unprecedented Stereochemical Inversion in the Elimination Reaction of a d-Amino Acid.Biochemistry. 2021 May 25;60(20):1609-1618. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.1c00106. Epub 2021 May 5. Biochemistry. 2021. PMID: 33949189 Free PMC article.
-
Properties and mechanism of d-glucosaminate-6-phosphate ammonia-lyase: An aminotransferase family enzyme with d-amino acid specificity.Biochim Biophys Acta Proteins Proteom. 2018 Jul;1866(7):799-805. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2017.12.006. Epub 2017 Dec 23. Biochim Biophys Acta Proteins Proteom. 2018. PMID: 29277660
-
Corrigendum: His-163 is a stereospecific proton donor in the mechanism of d-glucosaminate-6-phosphate ammonia-lyase.FEBS Lett. 2022 Dec;596(23):3103. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.14517. Epub 2022 Oct 25. FEBS Lett. 2022. PMID: 36281965 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
The role of substrate strain in the mechanism of the carbon-carbon lyases.Bioorg Chem. 2014 Dec;57:198-205. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2014.06.002. Epub 2014 Jun 28. Bioorg Chem. 2014. PMID: 25035301 Review.
-
Friedel-Crafts-type mechanism for the enzymatic elimination of ammonia from histidine and phenylalanine.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2005 Jun 13;44(24):3668-88. doi: 10.1002/anie.200461377. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2005. PMID: 15906398 Review.
References
-
- Phillips RS, Ting SC, Tetsadjio AG, Anderson KL, Friez KM, Miller KA, et al. Properties and mechanism of D‐glucosaminate‐6‐phosphate ammonia‐lyase: an aminotransferase family enzyme with D‐amino acid specificity. Biochim Biophys Acta Proteins Proteomics. 2018;1866:799–805. - PubMed
-
- Phillips RS, Ting SCK, Anderson K. Structure and mechanism of d‐Glucosaminate‐6‐phosphate ammonia‐lyase: a novel octameric assembly for a pyridoxal 5′‐phosphate‐dependent enzyme, and unprecedented stereochemical inversion in the elimination reaction of a D‐amino acid. Biochemistry. 2021;60:1609–18. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Studier FW. Protein production by auto‐induction in high‐density shaking cultures. Protein Expr Purif. 2005;41:207–34. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

