The application of Caprini Risk Assessment Model in evaluation of deep vein thrombosis for patients with end-stage osteoarthritis before arthroplasty
- PMID: 35953802
- PMCID: PMC9373495
- DOI: 10.1186/s12891-022-05712-z
The application of Caprini Risk Assessment Model in evaluation of deep vein thrombosis for patients with end-stage osteoarthritis before arthroplasty
Abstract
Background: Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) was a fatal complication of knee arthroplasty. We had neglected the risk factors of preoperative DVT although patients undergoing knee arthroplasty were at high risk for VTE. This study was to determine the risk factors for preoperative DVT and application of Caprini Risk Assessment Model (RAM) in patients with end-stage knee osteoarthritis (OA).
Methods: We retrospectively analyzed 1808 cases with end-stage knee OA undergoing primary knee arthroplasty from May 2015 to December 2020. Based on the results of ultrasonography in lower extremities, all patients were divided into non-DVT group and DVT group. Distribution of risk factors and risk levels were compared using χ2 test between two groups. Binary logistic regression analysis was used to determine the risk factors and relationship of risk levels and preoperative DVT.
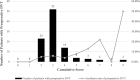
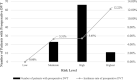
Results: The incidence of preoperative DVT was 5.53% (n = 100). Distribution of the study population by risk level was low, 4.09%; moderate, 23.95%; high, 66.98%; and highest 4.98%. Female (P = 0.002), age (P = 0.012), swollen legs (P = 0.035) and history of blood clots (P < 0.001) was correlated with preoperative DVT. Difference among four risk levels was significant (P = 0.007). Patients with highest risk level had statistically significant association with preoperative DVT (P = 0.005, OR = 2.93, 95%CI [1.375-6.246]).
Conclusion: The incidence of preoperative DVT was 5.53% in end-stage knee OA patients. The gender (female) and age were independent risk factors for preoperative DVT. The risk group classification by Caprini RAM was significantly associated with preoperative DVT. The usage of Caprini RAM before knee arthroplasty may be beneficial for prophylaxis of DVT.
Keywords: Caprini RAM; Knee arthroplasty; Preoperative deep vein thrombosis.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Qing Jiang is a member of the editorial board (Section Editor) of BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders. The authors declare that they have no competing of interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Incidence of and risk factors for preoperative deep vein thrombosis in elderly patients with end-stage osteoarthritis following total knee arthroplasty: a retrospective cohort study.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024 Oct 1;25(1):754. doi: 10.1186/s12891-024-07871-7. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024. PMID: 39354450 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying high-risk groups for deep vein thrombosis after primary total knee arthroplasty using preoperative Caprini scores and D-dimer levels.J Orthop Surg Res. 2024 Oct 1;19(1):616. doi: 10.1186/s13018-024-05074-3. J Orthop Surg Res. 2024. PMID: 39350206 Free PMC article.
-
Integrating D-Dimer Thresholds into the Revised Caprini Risk Stratification to Predict Deep Vein Thrombosis Risk in Preoperative Knee Osteoarthritis Patients.Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2025 Jan-Dec;31:10760296241311265. doi: 10.1177/10760296241311265. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2025. PMID: 39784945 Free PMC article.
-
Preoperative risk factors for deep vein thrombosis in knee osteoarthritis patients undergoing total knee arthroplasty.J Orthop Sci. 2023 Jan;28(1):180-187. doi: 10.1016/j.jos.2021.09.016. Epub 2021 Oct 27. J Orthop Sci. 2023. PMID: 34716065
-
Influence of diabetes on the risk of deep vein thrombosis of patients after total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis.J Orthop Surg Res. 2024 Mar 4;19(1):164. doi: 10.1186/s13018-024-04624-z. J Orthop Surg Res. 2024. PMID: 38439085 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Long-term exposures to ambient particulate matter and ozone pollution with lower extremity deep vein thrombosis after surgical operations: a retrospective case-control study in Beijing, China.BMC Public Health. 2023 Oct 9;23(1):1956. doi: 10.1186/s12889-023-16882-3. BMC Public Health. 2023. PMID: 37814263 Free PMC article.
-
Development and validation of a novel screening tool for deep vein thrombosis in patients with spinal cord injury: A five-year cross-sectional study.Spinal Cord. 2024 Sep;62(9):523-531. doi: 10.1038/s41393-024-01014-4. Epub 2024 Jul 12. Spinal Cord. 2024. PMID: 38997421
-
Incidence of and risk factors for preoperative deep vein thrombosis in elderly patients with end-stage osteoarthritis following total knee arthroplasty: a retrospective cohort study.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024 Oct 1;25(1):754. doi: 10.1186/s12891-024-07871-7. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024. PMID: 39354450 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Memtsoudis SG, Della Valle AG, Besculides MC, Esposito M, Koulouvaris P, Salvati EA. Risk factors for perioperative mortality after lower extremity arthroplasty: a population-based study of 6,901,324 patient discharges. J Arthroplasty. 2010;25(1):19–26. doi: 10.1016/j.arth.2008.11.010. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Snyder MA, Sympson AN, Scheuerman CM, Gregg JL, Hussain LR. Efficacy in Deep Vein Thrombosis Prevention With Extended Mechanical Compression Device Therapy and Prophylactic Aspirin Following Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Randomized Control Trial. J Arthroplasty. 2017;32(5):1478–1482. doi: 10.1016/j.arth.2016.12.027. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical