Effects of Cinnamon Essential Oil on Oxidative Damage and Outer Membrane Protein Genes of Salmonella enteritidis Cells
- PMID: 35954002
- PMCID: PMC9368406
- DOI: 10.3390/foods11152234
Effects of Cinnamon Essential Oil on Oxidative Damage and Outer Membrane Protein Genes of Salmonella enteritidis Cells
Abstract
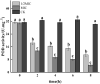
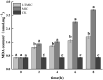
Salmonella is an important pathogen causing food poisoning. Food safety and health are the themes of today′s society. As a class of food-borne pathogens, Salmonella enteritidis had become one of the common zoonotic pathogens. Cinnamon essential oil (CEO) had been reported as an antibacterial agent, but there are few studies on its antibacterial mechanism. This study investigated the effects of CEO on oxidative damage and outer membrane protein genes of Salmonella enteritidis cells. First, the reactive oxygen species content in bacteria treated with different concentrations of cinnamon essential oil was determined by fluorescence spectrophotometry, and the effects of superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT) and superoxide dismutase (SOD), and catalase (CAT) and peroxidase (POD) were determined by the kit method. The activity of POD and the content of malondialdehyde (MDA) were investigated to investigate the oxidative damage of CEO to Salmonella enteritidis cells. By analyzing the effect of CEO on the Salmonella enteritidis cell membrane’s outer membrane protein gene expression, the mechanism of CEO′s action on the Salmonella enteritidis cell membrane was preliminarily discussed. The results showed that CEO treatment had an obvious oxidative damaging effect on Salmonella enteritidis. Compared with the control group, the increase in CEO concentration caused a significant increase in the bacteria ROS content. The observation technique experiment found that with the increase in CEO concentration, the number of stained cells increased, which indicated that CEO treatment would increase the ROS level in the cells, and it would also increase with the increase in CEO concentration, thus causing the oxidation of cells and damage. In addition, CEO treatment also caused the disruption of the balance of the cellular antioxidant enzymes (SOD, CAT, POD) system, resulting in an increase in the content of MDA, a membrane lipid metabolite, and increased protein carbonylation, which ultimately inhibited the growth of Salmonella enteritidis. The measurement results of cell membrane protein gene expression levels showed that the Omp genes to be detected in Salmonella enteritidis were all positive, which indicated that Salmonella enteritidis carried these four genes. Compared with the control group, the relative expressions of OmpF, OmpA and OmpX in the CEO treatment group were significantly increased (p < 0.05), which proved that the cell function was disturbed. Therefore, the toxicity of CEO to Salmonella enteritidis could be attributed to the damage of the cell membrane and the induction of oxidative stress at the same time. It was speculated that the antibacterial mechanism of CEO was the result of multiple effects. This work was expected to provide a theoretical basis for the development of new natural food preservatives and the prevention and control of Salmonella enteritidis.
Keywords: Salmonella enteritidis; cinnamon essential oil; outer membrane protein; oxidative damage.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Effects of cinnamon essential oil on the physiological metabolism of Salmonella enteritidis.Front Microbiol. 2022 Dec 6;13:1035894. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1035894. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36560942 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomics study unveils ROS balance in acid-adapted Salmonella Enteritidis.Food Microbiol. 2020 Dec;92:103585. doi: 10.1016/j.fm.2020.103585. Epub 2020 Jul 2. Food Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32950169
-
Antibacterial Effects of Ultrasound, Cinnamon Essential Oil, and Their Combination Against Listeria monocytogenes and Salmonella Typhimurium in Milk.J Food Sci. 2019 Dec;84(12):3700-3706. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.14914. Epub 2019 Nov 13. J Food Sci. 2019. PMID: 31721204
-
Iron oxide nanozyme suppresses intracellular Salmonella Enteritidis growth and alleviates infection in vivo.Theranostics. 2018 Nov 29;8(22):6149-6162. doi: 10.7150/thno.29303. eCollection 2018. Theranostics. 2018. PMID: 30613289 Free PMC article.
-
Encapsulation and delivery systems of cinnamon essential oil for food preservation applications.Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2023 Aug;318:102965. doi: 10.1016/j.cis.2023.102965. Epub 2023 Jul 17. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2023. PMID: 37480830 Review.
Cited by
-
Outer Membrane Porins Contribute to Antimicrobial Resistance in Gram-Negative Bacteria.Microorganisms. 2023 Jun 28;11(7):1690. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11071690. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 37512863 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Use of Star Anise-Cinnamon Essential Oil as an Alternative Antibiotic in Prevention of Salmonella Infections in Yellow Chickens.Antibiotics (Basel). 2022 Nov 9;11(11):1579. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11111579. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36358233 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic Potential of Cinnamon Oil: Chemical Composition, Pharmacological Actions, and Applications.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Dec 17;17(12):1700. doi: 10.3390/ph17121700. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39770541 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Essential Oils of Mentha arvensis and Cinnamomum cassia Exhibit Distinct Antibacterial Activity at Different Temperatures In Vitro and on Chicken Skin.Foods. 2023 Oct 27;12(21):3938. doi: 10.3390/foods12213938. Foods. 2023. PMID: 37959057 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Edible Coatings of Cassava Starch Incorporated with Clove and Cinnamon Essential Oils on the Shelf Life of Papaya.Membranes (Basel). 2023 Aug 31;13(9):772. doi: 10.3390/membranes13090772. Membranes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37755194 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pande M.V. Review of egg-related salmonellosis and reduction strategies in United States, Australia, United Kingdom and New Zealand. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2018;44:290–303. - PubMed
-
- Valdivieso-Ugarte M., Plaza-Díaz J., Gomez-Llorente C., Gómez E.L., Gil N. In vitro examination of antibacterial and immunomodulatory activities of cinnamon, white thyme, and clove essential oils. J. Funct. Foods. 2021;81:104436. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2021.104436. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

