Potential Cell-Based and Cell-Free Therapy for Patients with COVID-19
- PMID: 35954162
- PMCID: PMC9367488
- DOI: 10.3390/cells11152319
Potential Cell-Based and Cell-Free Therapy for Patients with COVID-19
Abstract
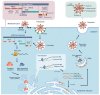
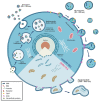
Since it was first reported, the novel coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) remains an unresolved puzzle for biomedical researchers in different fields. Various treatments, drugs, and interventions were explored as treatments for COVID. Nevertheless, there are no standard and effective therapeutic measures. Meanwhile, mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) therapy offers a new approach with minimal side effects. MSCs and MSC-based products possess several biological properties that potentially alleviate COVID-19 symptoms. Generally, there are three classifications of stem cell therapy: cell-based therapy, tissue engineering, and cell-free therapy. This review discusses the MSC-based and cell-free therapies for patients with COVID-19, their potential mechanisms of action, and clinical trials related to these therapies. Cell-based therapies involve the direct use and injection of MSCs into the target tissue or organ. On the other hand, cell-free therapy uses secreted products from cells as the primary material. Cell-free therapy materials can comprise cell secretomes and extracellular vesicles. Each therapeutic approach possesses different benefits and various risks. A better understanding of MSC-based and cell-free therapies is essential for supporting the development of safe and effective COVID-19 therapy.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; cell-based therapy; cell-free therapy; exosome; mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs); secretome.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mechanisms of Potential Therapeutic Utilization of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in COVID-19 Treatment.Cell Transplant. 2023 Jan-Dec;32:9636897231184611. doi: 10.1177/09636897231184611. Cell Transplant. 2023. PMID: 37395459 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stalling SARS-CoV2 infection with stem cells: can regenerating perinatal tissue mesenchymal stem cells offer a multi-tiered therapeutic approach to COVID-19?Placenta. 2022 Jan;117:161-168. doi: 10.1016/j.placenta.2021.12.005. Epub 2021 Dec 6. Placenta. 2022. PMID: 34915433 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mesenchymal stem cell-based treatments for COVID-19: status and future perspectives for clinical applications.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022 Feb 20;79(3):142. doi: 10.1007/s00018-021-04096-y. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022. PMID: 35187617 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potential application of mesenchymal stem cells and their exosomes in lung injury: an emerging therapeutic option for COVID-19 patients.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020 Oct 15;11(1):437. doi: 10.1186/s13287-020-01963-6. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020. PMID: 33059757 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mesenchymal stromal cells to fight SARS-CoV-2: Taking advantage of a pleiotropic therapy.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2021 Apr;58:114-133. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2020.12.002. Epub 2020 Dec 15. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2021. PMID: 33397585 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The impact understanding of exosome therapy in COVID-19 and preparations for the future approaches in dealing with infectious diseases and inflammation.Sci Rep. 2024 Mar 8;14(1):5724. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-56334-5. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38459174 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of Potential Therapeutic Utilization of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in COVID-19 Treatment.Cell Transplant. 2023 Jan-Dec;32:9636897231184611. doi: 10.1177/09636897231184611. Cell Transplant. 2023. PMID: 37395459 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Clinical Update on SARS-CoV-2: Pathology and Development of Potential Inhibitors.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023 Jan 4;45(1):400-433. doi: 10.3390/cimb45010028. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 36661514 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Progress in the Development of Stem Cell-Derived Cell-Free Therapies for Skin Aging.Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2023 Nov 22;16:3383-3406. doi: 10.2147/CCID.S434439. eCollection 2023. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2023. PMID: 38021432 Free PMC article. Review.
-
From Archipelago to Pandemic Battleground: Unveiling Indonesia's COVID-19 Crisis.J Epidemiol Glob Health. 2023 Dec;13(4):591-603. doi: 10.1007/s44197-023-00148-7. Epub 2023 Sep 14. J Epidemiol Glob Health. 2023. PMID: 37707715 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous