Human Milk Extracellular Vesicles: A Biological System with Clinical Implications
- PMID: 35954189
- PMCID: PMC9367292
- DOI: 10.3390/cells11152345
Human Milk Extracellular Vesicles: A Biological System with Clinical Implications
Abstract
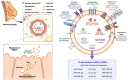
The consumption of human milk by a breastfeeding infant is associated with positive health outcomes, including lower risk of diarrheal disease, respiratory disease, otitis media, and in later life, less risk of chronic disease. These benefits may be mediated by antibodies, glycoproteins, glycolipids, oligosaccharides, and leukocytes. More recently, human milk extracellular vesicles (hMEVs) have been identified. HMEVs contain functional cargos, i.e., miRNAs and proteins, that may transmit information from the mother to promote infant growth and development. Maternal health conditions can influence hMEV composition. This review summarizes hMEV biogenesis and functional contents, reviews the functional evidence of hMEVs in the maternal-infant health relationship, and discusses challenges and opportunities in hMEV research.
Keywords: breastmilk; exosomes; extracellular vesicles; human milk; maternal–child health outcomes; non-coding RNAs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Prenatal SARS-CoV-2 Infection Alters Human Milk-Derived Extracellular Vesicles.Cells. 2025 Feb 15;14(4):284. doi: 10.3390/cells14040284. Cells. 2025. PMID: 39996756 Free PMC article.
-
Neonatal enteroids absorb extracellular vesicles from human milk-fed infant digestive fluid.J Extracell Vesicles. 2024 Apr;13(4):e12422. doi: 10.1002/jev2.12422. J Extracell Vesicles. 2024. PMID: 38602306 Free PMC article.
-
Non-Coding RNAs in Human Breast Milk: A Systematic Review.Front Immunol. 2021 Sep 1;12:725323. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.725323. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34539664 Free PMC article.
-
Prenatal SARS-CoV-2 infection alters postpartum human milk-derived extracellular vesicles.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Jun 1:2023.06.01.543234. doi: 10.1101/2023.06.01.543234. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Cells. 2025 Feb 15;14(4):284. doi: 10.3390/cells14040284. PMID: 37398231 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Unlocking the Secrets of Human Milk: Isolation and Characterization of Extracellular Vesicles.Adv Nutr. 2025 Jun;16(6):100430. doi: 10.1016/j.advnut.2025.100430. Epub 2025 Apr 25. Adv Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40288493 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Protective Role of Exosome-Derived MicroRNAs and Proteins from Human Breast Milk against Infectious Agents.Metabolites. 2023 May 8;13(5):635. doi: 10.3390/metabo13050635. Metabolites. 2023. PMID: 37233676 Free PMC article.
-
Human breast milk-derived exosomes and their positive role on neonatal intestinal health.Pediatr Res. 2025 Jul;98(1):72-79. doi: 10.1038/s41390-025-03813-8. Epub 2025 Jan 26. Pediatr Res. 2025. PMID: 39865171 Review.
-
Milk-borne small extracellular vesicles: kinetics and mechanisms of transport, distribution, and elimination.Extracell Vesicles Circ Nucl Acids. 2023 Sep;4(3):339-346. doi: 10.20517/evcna.2023.25. Epub 2023 Jul 12. Extracell Vesicles Circ Nucl Acids. 2023. PMID: 37829291 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in the isolation and characterization of milk-derived extracellular vesicles and their functions.Front Nutr. 2024 Dec 16;11:1512939. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1512939. eCollection 2024. Front Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39742102 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The maternal gut microbiome in pregnancy: implications for the developing immune system.Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 Jan;21(1):35-45. doi: 10.1038/s41575-023-00864-2. Epub 2023 Dec 14. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024. PMID: 38097774 Review.
References
-
- Panachan J., Rojsirikulchai N., Pongsakul N., Khowawisetsut L., Pongphitcha P., Siriboonpiputtana T., Chareonsirisuthigul T., Phornsarayuth P., Klinkulab N., Jinawath N., et al. Extracellular Vesicle-Based Method for Detecting MYCN Amplification Status of Pediatric Neuroblastoma. Cancers. 2022;14:2627. doi: 10.3390/cancers14112627. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

