Regulatory Roles of Noncoding RNAs in the Progression of Gastrointestinal Cancers and Health Disparities
- PMID: 35954293
- PMCID: PMC9367924
- DOI: 10.3390/cells11152448
Regulatory Roles of Noncoding RNAs in the Progression of Gastrointestinal Cancers and Health Disparities
Abstract
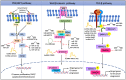
Annually, more than a million individuals are diagnosed with gastrointestinal (GI) cancers worldwide. With the advancements in radio- and chemotherapy and surgery, the survival rates for GI cancer patients have improved in recent years. However, the prognosis for advanced-stage GI cancers remains poor. Site-specific GI cancers share a few common risk factors; however, they are largely distinct in their etiologies and descriptive epidemiologic profiles. A large number of mutations or copy number changes associated with carcinogenesis are commonly found in noncoding DNA regions, which transcribe several noncoding RNAs (ncRNAs) that are implicated to regulate cancer initiation, metastasis, and drug resistance. In this review, we summarize the regulatory functions of ncRNAs in GI cancer development, progression, chemoresistance, and health disparities. We also highlight the potential roles of ncRNAs as therapeutic targets and biomarkers, mainly focusing on their ethnicity-/race-specific prognostic value, and discuss the prospects of genome-wide association studies (GWAS) to investigate the contribution of ncRNAs in GI tumorigenesis.
Keywords: biomarkers; chemoresistance; disparities; gastrointestinal cancers; noncoding RNAs; therapeutic targets.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
-
- Peery A.F., Crockett S.D., Murphy C.C., Jensen E.T., Kim H.P., Egberg M.D., Lund J.L., Moon A.M., Pate V., Barnes E.L., et al. Burden and Cost of Gastrointestinal, Liver, and Pancreatic Diseases in the United States: Update 2021. Gastroenterology. 2022;162:621–644. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.10.017. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

