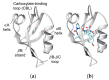
Three Binding Conformations of BIO124 in the Pocket of the PICK1 PDZ Domain
- PMID: 35954295
- PMCID: PMC9368557
- DOI: 10.3390/cells11152451
Three Binding Conformations of BIO124 in the Pocket of the PICK1 PDZ Domain
Abstract
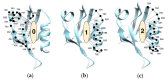
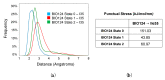
The PDZ family has drawn attention as possible drug targets because of the domains' wide ranges of function and highly conserved binding pockets. The PICK1 PDZ domain has been proposed as a possible drug target because the interactions between the PICK1 PDZ domain and the GluA2 subunit of the AMPA receptor have been shown to progress neurodegenerative diseases. BIO124 has been identified as a sub µM inhibitor of the PICK1-GluA2 interaction. Here, we use all-atom molecular dynamics simulations to reveal the atomic-level interaction pattern between the PICK1 PDZ domain and BIO124. Our simulations reveal three unique binding conformations of BIO124 in the PICK1 PDZ binding pocket, referred to here as state 0, state 1, and state 2. Each conformation is defined by a unique hydrogen bonding network and a unique pattern of hydrophobic interactions between BIO124 and the PICK1 PDZ domain. Interestingly, each conformation of BIO124 results in different dynamic changes to the PICK1 PDZ domain. Unlike states 1 and 2, state 0 induces dynamic coupling between BIO124 and the αA helix. Notably, this dynamic coupling with the αA helix is similar to what has been observed in other PDZ-ligand complexes. Our analysis indicates that the interactions formed between BIO124 and I35 may be the key to inducing dynamic coupling with the αA helix. Lastly, we suspect that the conformational shifts observed in our simulations may affect the stability and thus the overall effectiveness of BIO124. We propose that a physically larger inhibitor may be necessary to ensure sufficient interactions that permit stable binding between a drug and the PICK1 PDZ domain.
Keywords: BIO124; PDZ domain; PICK1; dynamic allosterism.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Investigating the allosteric response of the PICK1 PDZ domain to different ligands with all-atom simulations.Protein Sci. 2022 Dec;31(12):e4474. doi: 10.1002/pro.4474. Protein Sci. 2022. PMID: 36251217 Free PMC article.
-
Lock and chop: A novel method for the generation of a PICK1 PDZ domain and piperidine-based inhibitor co-crystal structure.Protein Sci. 2018 Mar;27(3):672-680. doi: 10.1002/pro.3361. Epub 2018 Jan 30. Protein Sci. 2018. PMID: 29280296 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a small-molecule inhibitor of the PICK1 PDZ domain that inhibits hippocampal LTP and LTD.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Jan 5;107(1):413-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0902225107. Epub 2009 Dec 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20018661 Free PMC article.
-
Protein interacting with C kinase and neurological disorders.Synapse. 2013 Aug;67(8):532-40. doi: 10.1002/syn.21657. Epub 2013 Mar 20. Synapse. 2013. PMID: 23436724 Review.
-
Structure and function of PICK1.Neurosignals. 2006-2007;15(4):190-201. doi: 10.1159/000098482. Epub 2007 Jan 11. Neurosignals. 2006. PMID: 17215589 Review.
Cited by
-
Investigating the allosteric response of the PICK1 PDZ domain to different ligands with all-atom simulations.Protein Sci. 2022 Dec;31(12):e4474. doi: 10.1002/pro.4474. Protein Sci. 2022. PMID: 36251217 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

