PTEN Dual Lipid- and Protein-Phosphatase Function in Tumor Progression
- PMID: 35954330
- PMCID: PMC9367293
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers14153666
PTEN Dual Lipid- and Protein-Phosphatase Function in Tumor Progression
Abstract
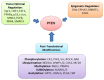
PTEN is the second most highly mutated tumor suppressor in cancer, following only p53. The PTEN protein functions as a phosphatase with lipid- and protein-phosphatase activity. PTEN-lipid-phosphatase activity dephosphorylates PIP3 to form PIP2, and it then antagonizes PI3K and blocks the activation of AKT, while its protein-phosphatase activity dephosphorylates different protein substrates and plays various roles in tumorigenesis. Here, we review the PTEN mutations and protein-phosphatase substrates in tumorigenesis and metastasis. Our purpose is to clarify how PTEN protein phosphatase contributes to its tumor-suppressive functions through PI3K-independent activities.
Keywords: PTEN; PTEN lipid phosphatase; PTEN protein phosphatase; PTEN protein substrate; metastasis; mutation; tumorigenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Gibas Z., Prout G.R., Jr., Connolly J.G., Pontes J.E., Sandberg A.A. Nonrandom chromosomal changes in transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder. Cancer Res. 1984;44:1257–1264. - PubMed
-
- Hsu S.C., Volpert O.V., Steck P.A., Mikkelsen T., Polverini P.J., Rao S., Chou P., Bouck N.P. Inhibition of an-gio-genesis in human glioblastomas by chromosome 10 induction of thrombospondin-1. Cancer Res. 1996;56:5684–5691. - PubMed
-
- Ittmann M. Allelic loss on chromosome 10 in prostate adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res. 1996;56:2143–2147. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

