Advances in the Current Understanding of the Mechanisms Governing the Acquisition of Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer
- PMID: 35954408
- PMCID: PMC9367587
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers14153744
Advances in the Current Understanding of the Mechanisms Governing the Acquisition of Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer
Abstract
Despite aggressive treatment and androgen-deprivation therapy, most prostate cancer patients ultimately develop castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC), which is associated with high mortality rates. However, the mechanisms governing the development of CRPC are poorly understood, and androgen receptor (AR) signaling has been shown to be important in CRPC through AR gene mutations, gene overexpression, co-regulatory factors, AR shear variants, and androgen resynthesis. A growing number of non-AR pathways have also been shown to influence the CRPC progression, including the Wnt and Hh pathways. Moreover, non-coding RNAs have been identified as important regulators of the CRPC pathogenesis. The present review provides an overview of the relevant literature pertaining to the mechanisms governing the molecular acquisition of castration resistance in prostate cancer, providing a foundation for future, targeted therapeutic efforts.
Keywords: Hh pathway; Wnt pathway; androgen receptor; destructive resistance prostate cancer; ncRNAs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

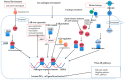
Similar articles
-
Understanding Mechanisms of Resistance in Metastatic Castration-resistant Prostate Cancer: The Role of the Androgen Receptor.Eur Urol Focus. 2016 Dec;2(5):499-505. doi: 10.1016/j.euf.2016.11.013. Epub 2016 Dec 9. Eur Urol Focus. 2016. PMID: 28723515 Review.
-
Mechanisms of resistance in castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC).Transl Androl Urol. 2015 Jun;4(3):365-80. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2223-4683.2015.05.02. Transl Androl Urol. 2015. PMID: 26814148 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Understanding the mechanisms of androgen deprivation resistance in prostate cancer at the molecular level.Eur Urol. 2015 Mar;67(3):470-9. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2014.09.049. Epub 2014 Oct 8. Eur Urol. 2015. PMID: 25306226 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Androgen receptor: what we know and what we expect in castration-resistant prostate cancer.Int Urol Nephrol. 2018 Oct;50(10):1753-1764. doi: 10.1007/s11255-018-1964-0. Epub 2018 Aug 20. Int Urol Nephrol. 2018. PMID: 30128923 Review.
-
A Tale of Two Signals: AR and WNT in Development and Tumorigenesis of Prostate and Mammary Gland.Cancers (Basel). 2017 Jan 27;9(2):14. doi: 10.3390/cancers9020014. Cancers (Basel). 2017. PMID: 28134791 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pro-oncogene FBI-1 inhibits the ferroptosis of prostate carcinoma PC-3 cells via the microRNA-324-3p/GPX4 axis.J Cancer. 2024 Jun 1;15(13):4097-4112. doi: 10.7150/jca.96306. eCollection 2024. J Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38947389 Free PMC article.
-
Dissecting the effects of androgen deprivation therapy on cadherin switching in advanced prostate cancer: A molecular perspective.Oncol Res. 2023 Jan 12;30(3):137-155. doi: 10.32604/or.2022.026074. eCollection 2022. Oncol Res. 2023. PMID: 37305018 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Let's Go 3D! New Generation of Models for Evaluating Drug Response and Resistance in Prostate Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 10;24(6):5293. doi: 10.3390/ijms24065293. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36982368 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Assessing the clinical outcomes of immunotherapy and docetaxel combinations in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer: a meta-analysis.BMC Cancer. 2025 Jul 14;25(1):1173. doi: 10.1186/s12885-025-14575-1. BMC Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40660223 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of NOLC1 in cancers and viral infection.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023 Sep;149(12):10593-10608. doi: 10.1007/s00432-023-04934-5. Epub 2023 Jun 9. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37296317 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Deng T., Cai L., Chen Z., Guo J. Analysis of the burden of prostate cancer in China in 1990 and 2017. New Med. 2020;30:252–259.
-
- Fang Y., Zhou X. Updates and interpretation of the 2020 guidelines on prostate cancer of European Association of Urology. Chin. J. Endourol. 2020;14:401–404.
-
- Cornford P., Bellmunt J., Bolla M., Briers E., de Santis M., Gross T., Henry A.M., Joniau S., Lam T.B., Mason M.D., et al. EAU-ESTRO-SIOG Guidelines on Prostate Cancer. Part II: Treatment of Relapsing, Metastatic, and Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. Eur. Urol. 2017;71:630–642. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2016.08.002. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

