Current Developments of Artificial Intelligence in Digital Pathology and Its Future Clinical Applications in Gastrointestinal Cancers
- PMID: 35954443
- PMCID: PMC9367360
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers14153780
Current Developments of Artificial Intelligence in Digital Pathology and Its Future Clinical Applications in Gastrointestinal Cancers
Abstract
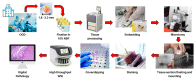
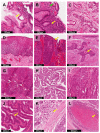
The implementation of DP will revolutionize current practice by providing pathologists with additional tools and algorithms to improve workflow. Furthermore, DP will open up opportunities for development of AI-based tools for more precise and reproducible diagnosis through computational pathology. One of the key features of AI is its capability to generate perceptions and recognize patterns beyond the human senses. Thus, the incorporation of AI into DP can reveal additional morphological features and information. At the current rate of AI development and adoption of DP, the interest in computational pathology is expected to rise in tandem. There have already been promising developments related to AI-based solutions in prostate cancer detection; however, in the GI tract, development of more sophisticated algorithms is required to facilitate histological assessment of GI specimens for early and accurate diagnosis. In this review, we aim to provide an overview of the current histological practices in AP laboratories with respect to challenges faced in image preprocessing, present the existing AI-based algorithms, discuss their limitations and present clinical insight with respect to the application of AI in early detection and diagnosis of GI cancer.
Keywords: algorithms; artificial intelligence; cancer diagnosis; computational pathology; deep learning; digital pathology; gastrointestinal tract; histopathology; machine learning; whole-slide imaging.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Whole Slide Imaging, Artificial Intelligence, and Machine Learning in Pediatric and Perinatal Pathology: Current Status and Future Directions.Pediatr Dev Pathol. 2025 Mar-Apr;28(2):91-98. doi: 10.1177/10935266241299073. Epub 2024 Nov 18. Pediatr Dev Pathol. 2025. PMID: 39552500 Review.
-
Requirements for implementation of artificial intelligence in the practice of gastrointestinal pathology.World J Gastroenterol. 2021 Jun 7;27(21):2818-2833. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i21.2818. World J Gastroenterol. 2021. PMID: 34135556 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Artificial Intelligence-Enabled Gastric Cancer Interpretations: Are We There yet?Surg Pathol Clin. 2023 Dec;16(4):673-686. doi: 10.1016/j.path.2023.05.005. Epub 2023 Jul 18. Surg Pathol Clin. 2023. PMID: 37863559 Review.
-
Artificial intelligence in digital histopathology for predicting patient prognosis and treatment efficacy in breast cancer.Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2024 May;24(5):363-377. doi: 10.1080/14737159.2024.2346545. Epub 2024 May 9. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2024. PMID: 38655907 Review.
-
Artificial intelligence in pathologic diagnosis, prognosis and prediction of prostate cancer.Am J Clin Exp Urol. 2024 Aug 25;12(4):200-215. doi: 10.62347/JSAE9732. eCollection 2024. Am J Clin Exp Urol. 2024. PMID: 39308594 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Artificial Intelligence-Driven Diagnosis of Pancreatic Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Oct 31;14(21):5382. doi: 10.3390/cancers14215382. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36358800 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeted Sequencing Approach and Its Clinical Applications for the Molecular Diagnosis of Human Diseases.Cells. 2023 Feb 2;12(3):493. doi: 10.3390/cells12030493. Cells. 2023. PMID: 36766834 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Artificial Intelligence-Assisted Diagnostic Cytology and Genomic Testing for Hematologic Disorders.Cells. 2023 Jun 30;12(13):1755. doi: 10.3390/cells12131755. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37443789 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Artificial intelligence: clinical applications and future advancement in gastrointestinal cancers.Front Artif Intell. 2024 Dec 20;7:1446693. doi: 10.3389/frai.2024.1446693. eCollection 2024. Front Artif Intell. 2024. PMID: 39764458 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Harnessing artificial intelligence for prostate cancer management.Cell Rep Med. 2024 Apr 16;5(4):101506. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2024.101506. Epub 2024 Apr 8. Cell Rep Med. 2024. PMID: 38593808 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Islami F., Goding Sauer A., Miller K.D., Siegel R.L., Fedewa S.A., Jacobs E.J., McCullough M.L., Patel A.V., Ma J., Soerjomataram I., et al. Proportion and number of cancer cases and deaths attributable to potentially modifiable risk factors in the United States. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018;68:31–54. doi: 10.3322/caac.21440. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

