Effects of an Online Supervised Exercise Training in Children with Obesity during the COVID-19 Pandemic
- PMID: 35954777
- PMCID: PMC9368250
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph19159421
Effects of an Online Supervised Exercise Training in Children with Obesity during the COVID-19 Pandemic
Abstract
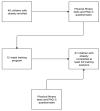
COVID-19 restrictions have dramatically reduced the active lifestyle and physical activity (PA) levels in the whole population, a situation that can contribute to weight gain and to develop obesity. To improve physical fitness (PF) in children with obesity during COVID-19 restrictions, sport specialists started to deliver physical training through tele-exercise. For these reasons, the aim of this study was to evaluate the effects of a 12-week online supervised training program in children with obesity on different PF components and PA levels. We enrolled a total of 40 Caucasian children (9 F/31 M; aged 11 ± 1.9 years) with obesity. The data collection consisted of a series of anthropometric measures, the PAQ-C questionnaire, and PF tests, valid and reliable tools to assess PF in children. We used a Wilcoxon's t-test and a Student's t-test, as appropriate, to assess the differences before and after the training protocol. A total of 37 patients completed the training protocol and were considered in the analysis. Our results show an improvement in all the PF tests, a reduction in the BMI z-score, the waist circumference, and in the waist-to-height ratio, and an increased PA level. In conclusion, the results of our study show that an online supervised training program is effective to promote PA, improving PF and reducing the BMI z-score in children with obesity.
Keywords: childhood exercise intervention; childhood obesity; online exercise; physical fitness.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
-
- Gatti A., Pugliese L., Carnevale Pellino V., Del Bianco M., Vandoni M., Lovecchio N. Self-Declared Physical Activity Levels and Self-Reported Physical Fitness in a Sample of Italian Adolescents during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Eur. J. Investig. Health Psychol. Educ. 2022;12:655–665. doi: 10.3390/ejihpe12060049. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dallolio L., Marini S., Masini A., Toselli S., Stagni R., Bisi M.C., Gori D., Tessari A., Sansavini A., Lanari M., et al. The Impact of COVID-19 on Physical Activity Behaviour in Italian Primary School Children: A Comparison before and during Pandemic Considering Gender Differences. BMC Public Health. 2022;22:52. doi: 10.1186/s12889-021-12483-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wijga A.H., Scholtens S., Bemelmans W.J.E., de Jongste J.C., Kerkhof M., Schipper M., Sanders E.A., Gerritsen J., Brunekreef B., Smit H.A. Comorbidities of Obesity in School Children: A Cross-Sectional Study in the PIAMA Birth Cohort. BMC Public Health. 2010;10:184. doi: 10.1186/1471-2458-10-184. - DOI - PMC - PubMed