Why Are Patients Unhappy with Their Healthcare? A Romanian Physicians' Perspective
- PMID: 35954821
- PMCID: PMC9368265
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph19159460
Why Are Patients Unhappy with Their Healthcare? A Romanian Physicians' Perspective
Abstract
Background: Medical professional liability complaints are not triggered by a single factor, but rather by multiple factors, each having more or less implications, such as the characteristics of the physician, the medical system, the patients, the complexity of their pathology, and the inherent limits of medicine. Knowledge about the factors that initiate the complaint procedure is essential to identify the targeted measures to limit their prevalence and impact. The purpose of this study was to identify the reasons behind the malpractice complaints and the factors that may influence the initiation of complaints by the patients.
Material and methods: This study was conducted using an online questionnaire, addressed to Romanian doctors, with questions about the reasons for patient dissatisfaction and complaints, the factors that predispose a physician to being complained against, and the protective factors against patient complaints.
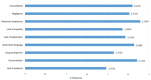
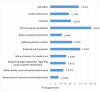
Results: The study group included 1684 physicians, of whom 16.1% were themselves involved in a complaint, and 52.5% knew of a colleague who was complained against. The opinions of the participants regarding the reasons for the complaints, the predisposing factors to complaints, and the factors that contributed to the reported incident showed a strong link between professional liability complaints and the physician-patient/patient's family relationship. The relationship between fellow physicians is additional to this.
Conclusion: This study reveals that the improvement in the relational aspects of medical practice (physician-patient relationship and relationship between physicians) has the highest potential to decrease the number of malpractice complaints. Its practical relevance is related to the need for training physicians in the relational aspects of medical practice during academic years and throughout their career.
Keywords: medical malpractice complaints; physicians’ perspective; reasons; relational aspects.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Reasons for and Facilitating Factors of Medical Malpractice Complaints. What Can Be Done to Prevent Them?Medicina (Kaunas). 2020 May 27;56(6):259. doi: 10.3390/medicina56060259. Medicina (Kaunas). 2020. PMID: 32471166 Free PMC article.
-
Beyond medical errors: exploring the interpersonal dynamics in physician-patient relationships linked to medico-legal complaints.BMC Health Serv Res. 2024 Aug 29;24(1):1003. doi: 10.1186/s12913-024-11457-3. BMC Health Serv Res. 2024. PMID: 39210366 Free PMC article.
-
The relation of patient satisfaction with complaints against physicians and malpractice lawsuits.Am J Med. 2005 Oct;118(10):1126-33. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2005.01.060. Am J Med. 2005. PMID: 16194644
-
Exploring the dynamics of physician-patient relationships: Factors affecting patient satisfaction and complaints.J Healthc Risk Manag. 2024 Apr;43(4):16-25. doi: 10.1002/jhrm.21567. Epub 2024 May 5. J Healthc Risk Manag. 2024. PMID: 38706117 Review.
-
Medical malpractice: the experience in Italy.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009 Feb;467(2):434-42. doi: 10.1007/s11999-008-0582-z. Epub 2008 Nov 5. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009. PMID: 18985423 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Medico-legal risk of infectious disease physicians in Canada: A retrospective review.J Assoc Med Microbiol Infect Dis Can. 2024 Jan 16;8(4):319-327. doi: 10.3138/jammi-2023-0022. eCollection 2024 Jan. J Assoc Med Microbiol Infect Dis Can. 2024. PMID: 38250623 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Verhoef L.M., Weenink J.W., Winters S., Robben P.B.M., Westert G., Kool R.B. The disciplined healthcare professional: A qualitative interview study on the impact of the disciplinary process and imposed meadures in the Netherlands. BMJ Open. 2015;5:e009275. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2015-009275. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Reason J. Human Error. Cambridge University Press; Cambridge, UK: 1990.
-
- Hanganu B., Ioan B.G. Malpraxisul medical: Cauze si consecinte asupra personalului medical [Medical malpractice: Causes and consequences on medical staff] In: Iorga M., Rosca C., editors. Psihologie Medicala. Studii Clinice [Medical Psychology. Clinical Studies] Editura Universitara; Bucharest, Romania: 2019. pp. 183–188. (In Romanian)
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources