Multidisciplinary Neuromuscular and Endurance Interventions on Youth Basketball Players: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis and Meta-Regression
- PMID: 35954997
- PMCID: PMC9368565
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph19159642
Multidisciplinary Neuromuscular and Endurance Interventions on Youth Basketball Players: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis and Meta-Regression
Abstract
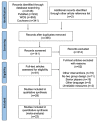
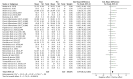
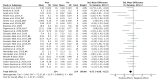
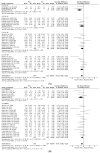
The main aims of this systematic review with meta-analysis and meta-regression were to describe the effect of multidisciplinary neuromuscular and endurance interventions, including plyometric training, mixed strength and conditioning, HIIT basketball programs and repeated sprint training on youth basketball players considering age, competitive level, gender and the type of the intervention performed to explore a predictive model through a meta-regression analysis. A structured search was conducted following PRISMA guidelines and PICOS model in Medline (PubMed), Web of Science (WOS) and Cochrane databases. Groups of experiments were created according to neuromuscular power (vertical; NPV and horizontal; NPH) and endurance (E). Meta-analysis and sub-groups analysis were performed using a random effect model and pooled standardized mean differences (SMD). A random effects meta-regression was performed regressing SMD for the different sub-groups against percentage change for NPV and NPH. There was a significant positive overall effect of the multidisciplinary interventions on NPV, NPH and E. Sub-groups analysis indicate differences in the effects of the interventions on NPV and NPH considering age, gender, competitive level and the type of the intervention used. Considering the current data available, the meta-regression analysis suggests a good predictability of U-16 and plyometric training on jump performance. Besides, male and elite level youth basketball players had a good predictability on multidirectional speed and agility performance.
Keywords: agility; basketball; junior; plyometrics; sport; training; young.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures









Similar articles
-
The Effects of Strength, Plyometric and Combined Training on Strength, Power and Speed Characteristics in High-Level, Highly Trained Male Youth Soccer Players: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Sports Med. 2024 Mar;54(3):623-643. doi: 10.1007/s40279-023-01944-8. Epub 2023 Oct 28. Sports Med. 2024. PMID: 37897637 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Plyometric Training Volume on Physical Performance in Youth Basketball Players.J Strength Cond Res. 2024 Jul 1;38(7):1275-1279. doi: 10.1519/JSC.0000000000004779. J Strength Cond Res. 2024. PMID: 38900173 Clinical Trial.
-
Vertical Versus Horizontal Training for Improving the Change of Direction Speed in Adult Basketball Players: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.J Strength Cond Res. 2024 Apr 1;38(4):791-803. doi: 10.1519/JSC.0000000000004674. Epub 2023 Dec 13. J Strength Cond Res. 2024. PMID: 38091370
-
The efficacy of Air Alert plyometric training program on enhancing biomotor skills in adolescent basketball players.Medicine (Baltimore). 2025 Feb 28;104(9):e41644. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000041644. Medicine (Baltimore). 2025. PMID: 40020108 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of Probiotic Supplementation on Exercise with Predominance of Aerobic Metabolism in Trained Population: A Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis and Meta-Regression.Nutrients. 2022 Jan 30;14(3):622. doi: 10.3390/nu14030622. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 35276980 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The effects of small-sided games on physical fitness in basketball players: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Sports Sci Med Rehabil. 2025 Jun 3;17(1):142. doi: 10.1186/s13102-025-01184-5. BMC Sports Sci Med Rehabil. 2025. PMID: 40462182 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of high-intensity interval training on selected indicators of physical fitness among male team-sport athletes: A systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2024 Nov 13;19(11):e0310955. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0310955. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39536016 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

