Evaluation of the Biocompatibility and Osteogenic Properties of Metal Oxide Coatings Applied by Magnetron Sputtering as Potential Biofunctional Surface Modifications for Orthopedic Implants
- PMID: 35955174
- PMCID: PMC9369574
- DOI: 10.3390/ma15155240
Evaluation of the Biocompatibility and Osteogenic Properties of Metal Oxide Coatings Applied by Magnetron Sputtering as Potential Biofunctional Surface Modifications for Orthopedic Implants
Abstract
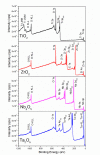
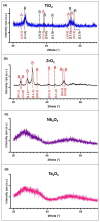
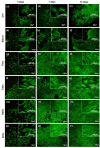
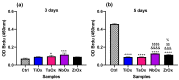
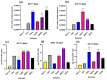
Biomaterials with adequate properties to direct a biological response are essential for orthopedic and dental implants. The surface properties are responsible for the biological response; thus, coatings with biologically relevant properties such as osteoinduction are exciting options to tailor the surface of different bulk materials. Metal oxide coatings such as TiO2, ZrO2, Nb2O5 and Ta2O5 have been suggested as promising for orthopedic and dental implants. However, a comparative study among them is still missing to select the most promising for bone-growth-related applications. In this work, using magnetron sputtering, TiO2, ZrO2, Ta2O5, and Nb2O5 thin films were deposited on Si (100) substrates. The coatings were characterized by Optical Profilometry, Scanning Electron Microscopy, Energy-Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy, X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy, X-ray Diffraction, Water Contact Angle measurements, and Surface Free Energy calculations. The cell adhesion, viability, proliferation, and differentiation toward the osteoblastic phenotype of mesenchymal stem cells plated on the coatings were measured to define the biological response. Results confirmed that all coatings were biocompatible. However, a more significant number of cells and proliferative cells were observed on Nb2O5 and Ta2O5 compared to TiO2 and ZrO2. Nevertheless, Nb2O5 and Ta2O5 seemed to induce cell differentiation toward the osteoblastic phenotype in a longer cell culture time than TiO2 and ZrO2.
Keywords: magnetron sputtering; mesenchymal stem cells; metal oxide coatings; osteogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Siti Nur Hazwani M.R., Lim L.X., Lockman Z., Zuhailawati H. Fabrication of Titanium-Based Alloys with Bioactive Surface Oxide Layer as Biomedical Implants: Opportunity and Challenges. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China Engl. Ed. 2022;32:1–44. doi: 10.1016/S1003-6326(21)65776-X. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

