Study on SO42-/Cl- Erosion Resistance and Mechanism of Recycled Concrete Containing Municipal Solid Waste Incineration (MSWI) Powder
- PMID: 35955289
- PMCID: PMC9369516
- DOI: 10.3390/ma15155352
Study on SO42-/Cl- Erosion Resistance and Mechanism of Recycled Concrete Containing Municipal Solid Waste Incineration (MSWI) Powder
Abstract
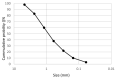
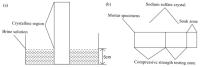
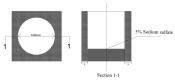
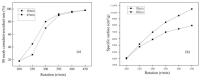
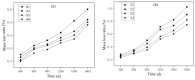
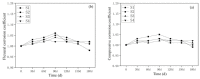
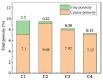
In this paper, the strength characteristics and erosion resistance of solid waste incineration (MSWI) powder were studied. Firstly, the optimum process for the preparation of regenerated powder from MSWI bottom slag by ball milling was determined as follows: rotational speed 350 r/min, time 45 min. The strength activity index of regenerated powder reached the maximum when the substitute content of powder was 30%. Secondly, the semi-erosion method was used to study the strength variation rule of mortar with different content of MSWI powder in semi-immersion of salt solution. It was found that the higher the content of MSWI powder, the greater the anti-erosion coefficient of mortar specimen. Finally, the capillary rise test, crystallization test and capillary pore water absorption test were used to study the total porosity, coarse capillary-pore porosity and fine-capillary pore porosity of concrete containing MSWI powder. The results showed that, with the increase in MSWI powder content, the above pore structure properties were improved. The results revealed the transport and crystallization process of salt solution in concrete mixed with MSWI powder and the mechanism of corrosion resistance.
Keywords: capillary migration parameters; municipal solid waste incineration (MSWI) powder; salt solution erosion; strength activity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures








References
-
- Chang H., Jin Z., Wang P., Wang J., Liu J. Comprehensive resistance of fair-faced concrete suffering from sulfate attack under marine environments. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021;277:122312.
-
- Zhang W., Xiao B., Hu D., Zhou H., Zheng J., Zhang F. Deterioration of the performance of cement mortar lining due to sulfate attack. Environ. Geotech. 2020;40:1–10. doi: 10.1680/jenge.18.00187. - DOI
-
- Dehwah H.A.F. Effect of sulfate concentration and associated cation type on concrete deterioration and morphological changes in cement hydrates. Constr. Build. Mater. 2007;21:29–39. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2005.07.010. - DOI
-
- Shahmansouri A.A., Akbarzadeh Bengar H., AzariJafari H. Life cycle assessment of eco-friendly concrete mixtures incorporating natural zeolite in sulfate-aggressive environment. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021;268:121136. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.121136. - DOI
-
- Cheng Y., Dong Y., Diao J., Zhang G., Chen C., Wu D. MSWI Bottom Ash Application to Resist Sulfate Attack on Concrete. Appl. Sci. 2019;9:5091. doi: 10.3390/app9235091. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

