Recent Advances in Adsorptive Nanocomposite Membranes for Heavy Metals Ion Removal from Contaminated Water: A Comprehensive Review
- PMID: 35955327
- PMCID: PMC9369589
- DOI: 10.3390/ma15155392
Recent Advances in Adsorptive Nanocomposite Membranes for Heavy Metals Ion Removal from Contaminated Water: A Comprehensive Review
Abstract
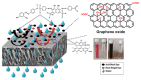
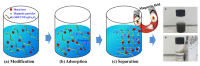
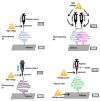
Water contamination is one of the most urgent concerns confronting the world today. Heavy metal poisoning of aquatic systems has piqued the interest of various researchers due to the high toxicity and carcinogenic consequences it has on living organisms. Due to their exceptional attributes such as strong reactivity, huge surface area, and outstanding mechanical properties, nanomaterials are being produced and employed in water treatment. In this review, recent advances in the use of nanomaterials in nanoadsorptive membrane systems for wastewater treatment and heavy metal removal are extensively discussed. These materials include carbon-based nanostructures, metal nanoparticles, metal oxide nanoparticles, nanocomposites, and layered double hydroxide-based compounds. Furthermore, the relevant properties of the nanostructures and the implications on their performance for water treatment and contamination removal are highlighted. The hydrophilicity, pore size, skin thickness, porosity, and surface roughness of these nanostructures can help the water permeability of the nanoadsorptive membrane. Other properties such as surface charge modification and mechanical strength can improve the metal adsorption effectiveness of nanoadsorptive membranes during wastewater treatment. Various nanocomposite membrane fabrication techniques are also reviewed. This study is important because it gives important information on the roles of nanomaterials and nanostructures in heavy metal removal and wastewater treatment.
Keywords: adsorption; heavy metals removal; nanocomposite membranes; nanomaterials; water treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Adsorptive nanocomposite membranes for heavy metal remediation: Recent progresses and challenges.Chemosphere. 2019 Oct;232:96-112. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.05.174. Epub 2019 May 23. Chemosphere. 2019. PMID: 31152909 Review.
-
Adsorptive removal of heavy metals from aqueous solutions: Progress of adsorbents development and their effectiveness.Environ Res. 2024 Jun 15;251(Pt 1):118562. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2024.118562. Epub 2024 Mar 5. Environ Res. 2024. PMID: 38447605 Review.
-
Ongoing progress on novel nanocomposite membranes for the separation of heavy metals from contaminated water.Chemosphere. 2021 May;270:129421. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.129421. Epub 2020 Dec 28. Chemosphere. 2021. PMID: 33401070 Review.
-
Advanced Polymeric Nanocomposite Membranes for Water and Wastewater Treatment: A Comprehensive Review.Polymers (Basel). 2023 Jan 20;15(3):540. doi: 10.3390/polym15030540. Polymers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36771842 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Review on some metal oxide nanoparticles as effective adsorbent in wastewater treatment.Water Sci Technol. 2022 Jun;85(12):3370-3395. doi: 10.2166/wst.2022.153. Water Sci Technol. 2022. PMID: 35771052 Review.
Cited by
-
UV-Cured Chitosan-Based Hydrogels Strengthened by Tannic Acid for the Removal of Copper Ions from Water.Polymers (Basel). 2022 Nov 1;14(21):4645. doi: 10.3390/polym14214645. Polymers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36365654 Free PMC article.
-
Green and Superior Adsorbents Derived from Natural Plant Gums for Removal of Contaminants: A Review.Materials (Basel). 2022 Dec 25;16(1):179. doi: 10.3390/ma16010179. Materials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36614516 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Magnesium Oxide Nanoparticles for the Adsorption of Pentavalent Arsenic from Water: Effects of Calcination.Membranes (Basel). 2023 Apr 28;13(5):475. doi: 10.3390/membranes13050475. Membranes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37233536 Free PMC article.
-
End-of-Life Management Strategies for Fe-Mn Nanocomposites Used in Arsenic Removal from Water.Polymers (Basel). 2025 May 15;17(10):1353. doi: 10.3390/polym17101353. Polymers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40430649 Free PMC article.
-
Removal of Heavy Metals from Wastewaters and Other Aqueous Streams by Pressure-Driven Membrane Technologies: An Outlook on Reverse Osmosis, Nanofiltration, Ultrafiltration and Microfiltration Potential from a Bibliometric Analysis.Membranes (Basel). 2024 Aug 22;14(8):180. doi: 10.3390/membranes14080180. Membranes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39195432 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Renu , Agarwal M., Singh K. Heavy metal removal from wastewater using various adsorbents: A review. J. Water Reuse Desalination. 2017;7:387–419. doi: 10.2166/wrd.2016.104. - DOI
-
- Rahman M.M., Alam Tumpa M.A., Zehravi M., Sarker M.T., Yamin M., Islam M.R., Harun-Or-Rashid M., Ahmed M., Ramproshad S., Mondal B., et al. An Overview of Antimicrobial Stewardship Optimization: The Use of Antibiotics in Humans and Animals to Prevent Resistance. Antibiotics. 2022;11:667. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11050667. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

