The Multiple Roles of CD147 in the Development and Progression of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma: An Overview
- PMID: 35955471
- PMCID: PMC9369056
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23158336
The Multiple Roles of CD147 in the Development and Progression of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma: An Overview
Abstract
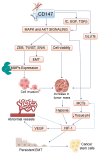
Cluster of differentiation (CD)147, also termed extracellular matrix metalloprotease inducer or basigin, is a glycoprotein ubiquitously expressed throughout the human body, the oral cavity included. CD147 actively participates in physiological tissue development or growth and has important roles in reactive processes such as inflammation, immunity, and tissue repair. It is worth noting that deregulated expression and/or activity of CD147 is observed in chronic inflammatory or degenerative diseases, as well as in neoplasms. Among the latter, oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) is characterized by an upregulation of CD147 in both the neoplastic and normal cells constituting the tumor mass. Most interestingly, the expression and/or activity of CD147 gradually increase as healthy oral mucosa becomes inflamed; hyperplastic/dysplastic lesions are then set on, and, eventually, OSCC develops. Based on these findings, here we summarize published studies which evaluate whether CD147 could be employed as a marker to monitor OSCC development and progression. Moreover, we describe CD147-promoted cellular and molecular events which are relevant to oral carcinogenesis, with the aim to provide useful information for assessing whether CD147 may be the target of novel therapeutic approaches directed against OSCC.
Keywords: CD147; EMT; cancer stem cells; hypoxia; inflammation; oral keratinocytes; oral premalignant diseases; oral squamous cell carcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
CD147 promotes proliferation and migration of oral cancer cells by inhibiting junctions between E-cadherin and β-catenin.J Oral Pathol Med. 2020 Nov;49(10):1019-1029. doi: 10.1111/jop.13088. Epub 2020 Aug 27. J Oral Pathol Med. 2020. PMID: 32740991
-
Clinical significance of Keap1 and Nrf2 in oral squamous cell carcinoma.PLoS One. 2013 Dec 27;8(12):e83479. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0083479. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24386210 Free PMC article.
-
CD147 promotes progression of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma via NF-kappa B signaling.J Cell Mol Med. 2019 Feb;23(2):954-966. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.13996. Epub 2018 Nov 12. J Cell Mol Med. 2019. PMID: 30421493 Free PMC article.
-
Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Concomitant Primary Tumors, What Do We Know? A Review of the Literature.Curr Oncol. 2023 Mar 27;30(4):3721-3734. doi: 10.3390/curroncol30040283. Curr Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37185396 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of CD147 (EMMPRIN/Basigin) in Tissue Remodeling.Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2020 Jun;303(6):1584-1589. doi: 10.1002/ar.24089. Epub 2019 Mar 15. Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2020. PMID: 30768865 Review.
Cited by
-
Biomarkers Identification in the Microenvironment of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Systematic Review of Proteomic Studies.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 16;25(16):8929. doi: 10.3390/ijms25168929. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39201614 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia signaling in cancer: HIF-1α stimulated by COVID-19 can lead to cancer progression and chemo-resistance in oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC).Discov Oncol. 2025 Mar 26;16(1):399. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-02150-w. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40138101 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The HIV Protease Inhibitor Ritonavir Reverts the Mesenchymal Phenotype Induced by Inflammatory Cytokines in Normal and Tumor Oral Keratinocytes to an Epithelial One, Increasing the Radiosensitivity of Tumor Oral Keratinocytes.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Jul 30;17(15):2519. doi: 10.3390/cancers17152519. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40805215 Free PMC article.
-
About a Possible Impact of Endodontic Infections by Fusobacterium nucleatum or Porphyromonas gingivalis on Oral Carcinogenesis: A Literature Overview.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 7;25(10):5083. doi: 10.3390/ijms25105083. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38791123 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Receptors and Cofactors That Contribute to SARS-CoV-2 Entry: Can Skin Be an Alternative Route of Entry?Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 26;24(7):6253. doi: 10.3390/ijms24076253. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37047226 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Panarese I., Aquino G., Ronchi A., Longo F., Montella M., Cozzolino I., Roccuzzo G., Colella G., Caraglia M., Franco R. Oral and Oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma: Prognostic and predictive parameters in the etiopathogenetic route. Expert Rev. Anticancer. 2019;19:105–119. doi: 10.1080/14737140.2019.1561288. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Gondivkar S.M., Gadbail A.R., Sarode S.C., Hedaoo A., Dasgupta S., Sharma B., Sharma A., Gondivkar R.S., Yuwanati M., Patil S., et al. Oral and general health-related quality of life in oral squamous cell carcinoma patients- comparative analysis of different treatment regims. J. Oral Biol. Craniofac. Res. 2021;11:125–131. doi: 10.1016/j.jobcr.2021.01.004. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

