TM4SF5-Mediated Regulation of Hepatocyte Transporters during Metabolic Liver Diseases
- PMID: 35955521
- PMCID: PMC9369364
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23158387
TM4SF5-Mediated Regulation of Hepatocyte Transporters during Metabolic Liver Diseases
Abstract
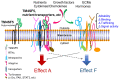
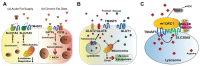
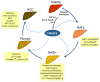
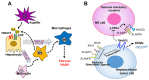
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is found in up to 30% of the world's population and can lead to hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), which has a poor 5-year relative survival rate of less than 40%. Clinical therapeutic strategies are not very successful. The co-occurrence of metabolic disorders and inflammatory environments during the development of steatohepatitis thus needs to be more specifically diagnosed and treated to prevent fatal HCC development. To improve diagnostic and therapeutic strategies, the identification of molecules and/or pathways responsible for the initiation and progression of chronic liver disease has been explored in many studies, but further study is still required. Transmembrane 4 L six family member 5 (TM4SF5) has been observed to play roles in the regulation of metabolic functions and activities in hepatocytes using in vitro cell and in vivo animal models without or with TM4SF5 expression in addition to clinical liver tissue samples. TM4SF5 is present on the membranes of different organelles or vesicles and cooperates with transporters for fatty acids, amino acids, and monocarbohydrates, thus regulating nutrient uptake into hepatocytes and metabolism and leading to phenotypes of chronic liver diseases. In addition, TM4SF5 can remodel the immune environment by interacting with immune cells during TM4SF5-mediated chronic liver diseases. Because TM4SF5 may act as an NAFLD biomarker, this review summarizes crosstalk between TM4SF5 and nutrient transporters in hepatocytes, which is related to chronic liver diseases.
Keywords: TM4SF5; amino acid transporter; fatty acid transporter; glucose/fructose transporter; hepatocyte; inflammation; metabolism; nonalcoholic fatty liver disease; protein–protein interaction; steatohepatitis; tetraspan(in).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
TM4SF5-dependent crosstalk between hepatocytes and macrophages to reprogram the inflammatory environment.Cell Rep. 2021 Nov 16;37(7):110018. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.110018. Cell Rep. 2021. PMID: 34788612
-
Crosstalk between TM4SF5 and GLUT8 regulates fructose metabolism in hepatic steatosis.Mol Metab. 2022 Apr;58:101451. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2022.101451. Epub 2022 Feb 2. Mol Metab. 2022. PMID: 35123128 Free PMC article.
-
Tetraspanin TM4SF5 in hepatocytes negatively modulates SLC27A transporters during acute fatty acid supply.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2021 Oct 15;710:109004. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2021.109004. Epub 2021 Aug 6. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2021. PMID: 34364885
-
Deranged hepatocyte intracellular Ca2+ homeostasis and the progression of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease to hepatocellular carcinoma.Cell Calcium. 2019 Sep;82:102057. doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2019.102057. Epub 2019 Jul 26. Cell Calcium. 2019. PMID: 31401389 Review.
-
Amino acid transporters as tetraspanin TM4SF5 binding partners.Exp Mol Med. 2020 Jan;52(1):7-14. doi: 10.1038/s12276-019-0363-7. Epub 2020 Jan 20. Exp Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 31956272 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Isoxazole-based molecules restore NK cell immune surveillance in hepatocarcinogenesis by targeting TM4SF5 and SLAMF7 linkage.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2025 Jan 20;10(1):15. doi: 10.1038/s41392-024-02106-6. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2025. PMID: 39828766 Free PMC article.
-
Overcoming Biological Barriers: Importance of Membrane Transporters in Homeostasis, Disease and Disease Treatment.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 13;24(8):7212. doi: 10.3390/ijms24087212. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37108379 Free PMC article.
-
Prevention of high-fat/high-sugar diet-induced type 2 diabetes mellitus-associated non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in rats with fermented and raw Rosa roxburghii Tratt (Cili) juice.Front Nutr. 2025 May 19;12:1584551. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1584551. eCollection 2025. Front Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40458826 Free PMC article.
-
Whole genome DNA methylation patterns in tissue and cfDNA associated with fibrosis reflect the complex signature of MASLD.PLoS One. 2025 Jul 17;20(7):e0328207. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0328207. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40674394 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatocyte TM4SF5-mediated cytosolic NCOA3 stabilization and macropinocytosis support albumin uptake and bioenergetics for hepatocellular carcinoma progression.Exp Mol Med. 2025 Apr;57(4):836-855. doi: 10.1038/s12276-025-01438-9. Epub 2025 Apr 4. Exp Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 40186033 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gawrieh S., Marion M.C., Komorowski R., Wallace J., Charlton M., Kissebah A., Langefeld C.D., Olivier M. Genetic variation in the peroxisome proliferator activated receptor-gamma gene is associated with histologically advanced NAFLD. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2012;57:952–957. doi: 10.1007/s10620-011-1994-2. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

