Relationship between Brain Metabolic Disorders and Cognitive Impairment: LDL Receptor Defect
- PMID: 35955522
- PMCID: PMC9369234
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23158384
Relationship between Brain Metabolic Disorders and Cognitive Impairment: LDL Receptor Defect
Abstract
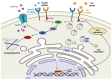
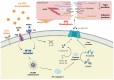
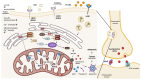
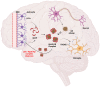
The low-density-lipoprotein receptor (LDLr) removes low-density lipoprotein (LDL), an endovascular transporter that carries cholesterol from the bloodstream to peripheral tissues. The maintenance of cholesterol content in the brain, which is important to protect brain function, is affected by LDLr. LDLr co-localizes with the insulin receptor and complements the internalization of LDL. In LDLr deficiency, LDL blood levels and insulin resistance increase, leading to abnormal cholesterol control and cognitive deficits in atherosclerosis. Defects in brain cholesterol metabolism lead to neuroinflammation and blood-brain-barrier (BBB) degradation. Moreover, interactions between endoplasmic reticulum stress (ER stress) and mitochondria are induced by ox-LDL accumulation, apolipoprotein E (ApoE) regulates the levels of amyloid beta (Aβ) in the brain, and hypoxia is induced by apoptosis induced by the LDLr defect. This review summarizes the association between neurodegenerative brain disease and typical cognitive deficits.
Keywords: ER stress; LDLr; SREBP; apoptosis; blood–brain-barrier (BBB) breakdown; cholesterol metabolism; insulin receptor; lectin-like oxidized LDL receptor-1 (LOX-1); mitochondria; neuroinflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
High Cholesterol Diet Exacerbates Blood-Brain Barrier Disruption in LDLr-/- Mice: Impact on Cognitive Function.J Alzheimers Dis. 2020;78(1):97-115. doi: 10.3233/JAD-200541. J Alzheimers Dis. 2020. PMID: 32925052 Free PMC article.
-
Increased susceptibility to amyloid-β-induced neurotoxicity in mice lacking the low-density lipoprotein receptor.J Alzheimers Dis. 2014;41(1):43-60. doi: 10.3233/JAD-132228. J Alzheimers Dis. 2014. PMID: 24577472
-
Cholesterol efflux via ATP-binding cassette transporter A1 (ABCA1) and cholesterol uptake via the LDL receptor influences cholesterol-induced impairment of beta cell function in mice.Diabetologia. 2010 Jun;53(6):1110-9. doi: 10.1007/s00125-010-1691-2. Epub 2010 Mar 13. Diabetologia. 2010. PMID: 20229095
-
Cholesterol in LDL receptor recycling and degradation.Clin Chim Acta. 2020 Jan;500:81-86. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2019.09.022. Epub 2019 Nov 23. Clin Chim Acta. 2020. PMID: 31770510 Review.
-
Low-density lipoprotein receptor (LDLR) family orchestrates cholesterol homeostasis.Yale J Biol Med. 2012 Mar;85(1):19-28. Epub 2012 Mar 29. Yale J Biol Med. 2012. PMID: 22461740 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
ERVW-1 Activates ATF6-Mediated Unfolded Protein Response by Decreasing GANAB in Recent-Onset Schizophrenia.Viruses. 2023 May 31;15(6):1298. doi: 10.3390/v15061298. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 37376599 Free PMC article.
-
Type-1-to-type-2 transition of brain microvascular pericytes induced by cytokines and disease-associated proteins: Role in neuroinflammation and blood-brain barrier disruption.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2025 Mar;45(3):405-420. doi: 10.1177/0271678X241296270. Epub 2024 Oct 30. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2025. PMID: 39473432 Free PMC article.
-
Association between cerebrovascular disease and perioperative neurocognitive disorders: a retrospective cohort study.Int J Surg. 2024 Jan 1;110(1):353-360. doi: 10.1097/JS9.0000000000000842. Int J Surg. 2024. PMID: 37916928 Free PMC article.
-
Carbon Nanodots Attenuate Lipid Peroxidation in the LDL Receptor Knockout Mouse Brain.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 May 11;12(5):1081. doi: 10.3390/antiox12051081. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37237947 Free PMC article.
-
The potential role of cholesterol in Parkinson's disease neuropathology: perpetrator or victim.Neurol Sci. 2023 Nov;44(11):3781-3794. doi: 10.1007/s10072-023-06926-2. Epub 2023 Jul 10. Neurol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37428278 Review.
References
-
- Ramakrishnan G., Arjuman A., Suneja S., Das C., Chandra N.C. The association between insulin and low-density lipoprotein receptors. Diabetes Vasc. Dis. Res. 2012;9:196–204. - PubMed
-
- Wade D.P., Knight B.L., Soutar A.K. Hormonal regulation of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) receptor activity in human hepatoma Hep G2 cells: Insulin increases LDL receptor activity and diminishes its suppression by exogenous LDL. Eur. J. Biochem. 1988;174:213–218. - PubMed
-
- Goritz C., Mauch D.H., Pfrieger F.W. Multiple mechanisms mediate cholesterol-induced synaptogenesis in a CNS neuron. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2005;29:190–201. - PubMed
-
- Pfenninger K.H. Plasma membrane expansion: A neuron’s Herculean task. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2009;10:251–261. - PubMed
-
- Takamori S., Holt M., Stenius K., Lemke E.A., Grønborg M., Riedel D., Urlaub H., Schenck S., Brügger B., Ringler P., et al. Molecular anatomy of a trafficking organelle. Cell. 2006;127:831–846. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

