Molecular Framework of Mouse Endothelial Cell Dysfunction during Inflammation: A Proteomics Approach
- PMID: 35955534
- PMCID: PMC9369400
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23158399
Molecular Framework of Mouse Endothelial Cell Dysfunction during Inflammation: A Proteomics Approach
Abstract
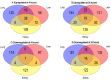
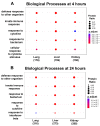
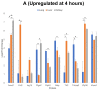
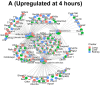
A key aspect of cytokine-induced changes as observed in sepsis is the dysregulated activation of endothelial cells (ECs), initiating a cascade of inflammatory signaling leading to leukocyte adhesion/migration and organ damage. The therapeutic targeting of ECs has been hampered by concerns regarding organ-specific EC heterogeneity and their response to inflammation. Using in vitro and in silico analysis, we present a comprehensive analysis of the proteomic changes in mouse lung, liver and kidney ECs following exposure to a clinically relevant cocktail of proinflammatory cytokines. Mouse lung, liver and kidney ECs were incubated with TNF-α/IL-1β/IFN-γ for 4 or 24 h to model the cytokine-induced changes. Quantitative label-free global proteomics and bioinformatic analysis performed on the ECs provide a molecular framework for the EC response to inflammatory stimuli over time and organ-specific differences. Gene Ontology and PANTHER analysis suggest why some organs are more susceptible to inflammation early on, and show that, as inflammation progresses, some protein expression patterns become more uniform while additional organ-specific proteins are expressed. These findings provide an in-depth understanding of the molecular changes involved in the EC response to inflammation and can support the development of drugs targeting ECs within different organs. Data are available via ProteomeXchange (identifier PXD031804).
Keywords: endothelium; inflammation; organ heterogeneity; proteomics.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflict of interest that could be perceived as prejudicing the impartiality of the research reported. Michael Rossi contributed to this manuscript while working at CFD Research Corp. Rossi is now employed at Illumina, Inc. (5200 Illumina Way, San Diego, CA, 92122).
Figures








Similar articles
-
Integrated proteomic analysis of tumor necrosis factor α and interleukin 1β-induced endothelial inflammation.J Proteomics. 2019 Feb 10;192:89-101. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2018.08.011. Epub 2018 Aug 25. J Proteomics. 2019. PMID: 30153514
-
Endothelial cell apicobasal polarity coordinates distinct responses to luminally versus abluminally delivered TNF-α in a microvascular mimetic.Integr Biol (Camb). 2020 Nov 18;12(11):275-289. doi: 10.1093/intbio/zyaa022. Integr Biol (Camb). 2020. PMID: 33164044 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-19 decreases leukocyte-endothelial cell interactions by reduction in endothelial cell adhesion molecule mRNA stability.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2013 Aug 1;305(3):C255-65. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00069.2013. Epub 2013 Apr 17. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23596173 Free PMC article.
-
Structural pathways for macromolecular and cellular transport across the blood-brain barrier during inflammatory conditions. Review.Histol Histopathol. 2004 Apr;19(2):535-64. doi: 10.14670/HH-19.535. Histol Histopathol. 2004. PMID: 15024715 Review.
-
Endothelial Responses in Sepsis.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2020 Aug 1;202(3):361-370. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201910-1911TR. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2020. PMID: 32101446 Review.
Cited by
-
Emerging roles of lactate in acute and chronic inflammation.Cell Commun Signal. 2024 May 16;22(1):276. doi: 10.1186/s12964-024-01624-8. Cell Commun Signal. 2024. PMID: 38755659 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evolving Paradigms in Sepsis Management: A Narrative Review.Cells. 2024 Jul 9;13(14):1172. doi: 10.3390/cells13141172. Cells. 2024. PMID: 39056754 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Understanding human aging and the fundamental cell signaling link in age-related diseases: the middle-aging hypovascularity hypoxia hypothesis.Front Aging. 2023 Jun 13;4:1196648. doi: 10.3389/fragi.2023.1196648. eCollection 2023. Front Aging. 2023. PMID: 37384143 Free PMC article.
-
Sustained caloric restriction potentiates insulin action by activating prostacyclin synthase.Obesity (Silver Spring). 2024 Dec;32(12):2286-2298. doi: 10.1002/oby.24150. Epub 2024 Oct 17. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2024. PMID: 39420421 Free PMC article.
-
Commonly disrupted pathways in brain and kidney in a pig model of systemic endotoxemia.J Neuroinflammation. 2024 Jan 4;21(1):9. doi: 10.1186/s12974-023-03002-6. J Neuroinflammation. 2024. PMID: 38178237 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

