BDNF Therapeutic Mechanisms in Neuropsychiatric Disorders
- PMID: 35955546
- PMCID: PMC9368938
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23158417
BDNF Therapeutic Mechanisms in Neuropsychiatric Disorders
Abstract
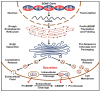
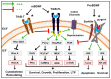
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) is the most abundant neurotrophin in the adult brain and functions as both a primary neurotrophic signal and a neuromodulator. It serves essential roles in neuronal development, maintenance, transmission, and plasticity, thereby influencing aging, cognition, and behavior. Accumulating evidence associates reduced central and peripheral BDNF levels with various neuropsychiatric disorders, supporting its potential utilization as a biomarker of central pathologies. Subsequently, extensive research has been conducted to evaluate restoring, or otherwise augmenting, BDNF transmission as a potential therapeutic approach. Promising results were indeed observed for genetic BDNF upregulation or exogenous administration using a multitude of murine models of neurological and psychiatric diseases. However, varying mechanisms have been proposed to underlie the observed therapeutic effects, and many findings indicate the engagement of disease-specific and other non-specific mechanisms. This is because BDNF essentially affects all aspects of neuronal cellular function through tropomyosin receptor kinase B (TrkB) receptor signaling, the disruptions of which vary between brain regions across different pathologies leading to diversified consequences on cognition and behavior. Herein, we review the neurophysiology of BDNF transmission and signaling and classify the converging and diverging molecular mechanisms underlying its therapeutic potentials in neuropsychiatric disorders. These include neuroprotection, synaptic maintenance, immunomodulation, plasticity facilitation, secondary neuromodulation, and preservation of neurovascular unit integrity and cellular viability. Lastly, we discuss several findings suggesting BDNF as a common mediator of the therapeutic actions of centrally acting pharmacological agents used in the treatment of neurological and psychiatric illness.
Keywords: TrkB signaling; brain-derived neurotrophic factor; neurodegeneration; neuroinflammation; neuromodulation; neuroprotection; oxidative stress; synaptic plasticity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Role of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor as an Essential Mediator in Neuronal Functions and the Therapeutic Potential of Its Mimetics for Neuroprotection in Neurologic and Psychiatric Disorders.Molecules. 2025 Feb 12;30(4):848. doi: 10.3390/molecules30040848. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40005159 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TrkB/BDNF signaling pathway and its small molecular agonists in CNS injury.Life Sci. 2024 Jan 1;336:122282. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2023.122282. Epub 2023 Nov 24. Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 38008209 Review.
-
Integral Characterization of Defective BDNF/TrkB Signalling in Neurological and Psychiatric Disorders Leads the Way to New Therapies.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Jan 28;18(2):268. doi: 10.3390/ijms18020268. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28134845 Free PMC article. Review.
-
BDNF function and intracellular signaling in neurons.Histol Histopathol. 2010 Feb;25(2):237-58. doi: 10.14670/HH-25.237. Histol Histopathol. 2010. PMID: 20017110 Review.
-
BDNF-induced local protein synthesis and synaptic plasticity.Neuropharmacology. 2014 Jan;76 Pt C:639-56. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.04.005. Epub 2013 Apr 16. Neuropharmacology. 2014. PMID: 23602987 Review.
Cited by
-
The Compelling Role of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Signaling in Multiple Sclerosis: Role of BDNF Activators.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024 Dec;30(12):e70167. doi: 10.1111/cns.70167. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024. PMID: 39654365 Free PMC article. Review.
-
BDNF/TrkB activators in Parkinson's disease: A new therapeutic strategy.J Cell Mol Med. 2024 May;28(10):e18368. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.18368. J Cell Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 38752280 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Centella asiatica extract ameliorates deoxygenation-induced neurological dysfunction in zebrafish larvae.Open Vet J. 2024 May;14(5):1154-1160. doi: 10.5455/OVJ.2024.v14.i5.9. Epub 2024 May 31. Open Vet J. 2024. PMID: 38938421 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing Causality Between Plasma Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor With Major Depression Disorder: A Bidirectional Mendelian Randomization Study.Brain Behav. 2025 Mar;15(3):e70425. doi: 10.1002/brb3.70425. Brain Behav. 2025. PMID: 40103195 Free PMC article.
-
BDNF Unveiled: Exploring Its Role in Major Depression Disorder Serotonergic Imbalance and Associated Stress Conditions.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Aug 3;15(8):2081. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15082081. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37631295 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources