A Multistage In Silico Study of Natural Potential Inhibitors Targeting SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease
- PMID: 35955547
- PMCID: PMC9369012
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23158407
A Multistage In Silico Study of Natural Potential Inhibitors Targeting SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease
Abstract
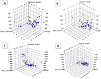
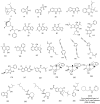
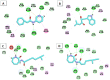
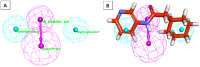
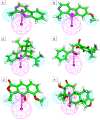
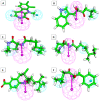
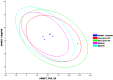
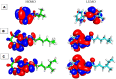
Among a group of 310 natural antiviral natural metabolites, our team identified three compounds as the most potent natural inhibitors against the SARS-CoV-2 main protease (PDB ID: 5R84), Mpro. The identified compounds are sattazolin and caprolactin A and B. A validated multistage in silico study was conducted using several techniques. First, the molecular structures of the selected metabolites were compared with that of GWS, the co-crystallized ligand of Mpro, in a structural similarity study. The aim of this study was to determine the thirty most similar metabolites (10%) that may bind to the Mpro similar to GWS. Then, molecular docking against Mpro and pharmacophore studies led to the choice of five metabolites that exhibited good binding modes against the Mpro and good fit values against the generated pharmacophore model. Among them, three metabolites were chosen according to ADMET studies. The most promising Mpro inhibitor was determined by toxicity and DFT studies to be caprolactin A (292). Finally, molecular dynamics (MD) simulation studies were performed for caprolactin A to confirm the obtained results and understand the thermodynamic characteristics of the binding. It is hoped that the accomplished results could represent a positive step in the battle against COVID-19 through further in vitro and in vivo studies on the selected compounds.
Keywords: ADMET; DFT; MD simulations; SARS-CoV-2; docking; main protease; pharmacophoric; structural similarity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Multi-Step In Silico Discovery of Natural Drugs against COVID-19 Targeting Main Protease.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jun 21;23(13):6912. doi: 10.3390/ijms23136912. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35805916 Free PMC article.
-
Optimization Rules for SARS-CoV-2 Mpro Antivirals: Ensemble Docking and Exploration of the Coronavirus Protease Active Site.Viruses. 2020 Aug 26;12(9):942. doi: 10.3390/v12090942. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 32859008 Free PMC article.
-
Reckoning a fungal metabolite, Pyranonigrin A as a potential Main protease (Mpro) inhibitor of novel SARS-CoV-2 virus identified using docking and molecular dynamics simulation.Biophys Chem. 2020 Sep;264:106425. doi: 10.1016/j.bpc.2020.106425. Epub 2020 Jul 6. Biophys Chem. 2020. PMID: 32663708 Free PMC article.
-
In silico prediction of potential inhibitors for the main protease of SARS-CoV-2 using molecular docking and dynamics simulation based drug-repurposing.J Infect Public Health. 2020 Sep;13(9):1210-1223. doi: 10.1016/j.jiph.2020.06.016. Epub 2020 Jun 16. J Infect Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32561274 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease for Treatment of COVID-19: Covalent Inhibitors Structure-Activity Relationship Insights and Evolution Perspectives.J Med Chem. 2022 Oct 13;65(19):12500-12534. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.2c01005. Epub 2022 Sep 28. J Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 36169610 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Green Synthesized Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Based on Cestrum diurnum L. of Potential Antiviral Activity against Human Corona 229-E Virus.Molecules. 2022 Dec 28;28(1):266. doi: 10.3390/molecules28010266. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36615461 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis, biological evaluation and computer-aided discovery of new thiazolidine-2,4-dione derivatives as potential antitumor VEGFR-2 inhibitors.RSC Adv. 2023 Sep 19;13(40):27801-27827. doi: 10.1039/d3ra05689a. eCollection 2023 Sep 18. RSC Adv. 2023. PMID: 37731835 Free PMC article.
-
Design, synthesis, docking, MD simulations, and anti-proliferative evaluation of thieno[2,3-d]pyrimidine derivatives as new EGFR inhibitors.J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2023 Dec;38(1):2220579. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2023.2220579. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 37288786 Free PMC article.
-
(E)-N-(3-(1-(2-(4-(2,2,2-Trifluoroacetamido)benzoyl)hydrazono)ethyl)phenyl)nicotinamide: A Novel Pyridine Derivative for Inhibiting Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor-2: Synthesis, Computational, and Anticancer Studies.Molecules. 2022 Nov 9;27(22):7719. doi: 10.3390/molecules27227719. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36431818 Free PMC article.
-
Anticancer derivative of the natural alkaloid, theobromine, inhibiting EGFR protein: Computer-aided drug discovery approach.PLoS One. 2023 Mar 9;18(3):e0282586. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0282586. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 36893122 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. [(accessed on 19 January 2022)]. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/
-
- De Groot R.J., Baker S.C., Baric R.S., Brown C.S., Drosten C., Enjuanes L., Fouchier R.A., Galiano M., Gorbalenya A.E., Memish Z.A. Commentary: Middle east respiratory syndrome coronavirus (mers-cov): Announcement of the coronavirus study group. J. Virol. 2013;87:7790–7792. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01244-13. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhang S. Computer-aided drug discovery and development. Drug Des. Discov. 2011;716:23–38. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

