Persistent TLR4 Activation Promotes Hepatocellular Carcinoma Growth through Positive Feedback Regulation by LIN28A/Let-7g miRNA
- PMID: 35955552
- PMCID: PMC9369227
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23158419
Persistent TLR4 Activation Promotes Hepatocellular Carcinoma Growth through Positive Feedback Regulation by LIN28A/Let-7g miRNA
Abstract
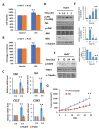
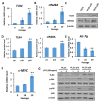
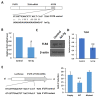
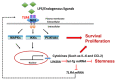
Chronic inflammation caused by liver damage or infection plays an important role in the development and progression of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). The activation of Toll-like receptors 4 (TLR4) is involved in HCC tumorigenesis. Moreover, high TLR4 expression in HCC has been linked to poor prognosis. Although the expression of TLR4 in HCC is relatively low compared to hematopoietic cells, it is important to explore the molecular mechanism leading to the elevation of TLR4 in HCC. In this study, we aimed to investigate the positive regulating loop for TLR4 expression in HCC in response to chronic inflammation. Our results confirm that the mRNA expression of TLR4 and proinflammatory cytokines, including interleukin 6 (IL6) and C-C motif chemokine ligand 2 (CCL2), positively correlate in human HCC samples. High TLR4 expression in HCC is more susceptible to lipopolysaccharide (LPS); TLR4 activation in HCC provides growth and survival advantages and thus promotes tumorigenesis. It has been shown that the LIN28/let-7 microRNA (miRNA) axis is a downstream effector of the TLR4 signal pathway, and let-7 miRNA is a potential post-transcriptional regulator for TLR4. Thus, we investigated the correlation between TLR4 and LIN28A mRNA and let-7g miRNA in HCC clinical samples and found that the expression of TLR4 was positively correlated with LIN28A and negatively correlated with let-7g miRNA. Moreover, by culturing PLC/PRF5 (PLC5) HCC cells in low-dose LPS-containing medium to mimic chronic inflammation for persistent TLR4 activation, the mRNA and protein levels of TLR4 and LIN28A were elevated, and let-7g miRNA was decreased. Furthermore, the 3' untranslated region (3'UTR) of TLR4 mRNA was shown to be the target of let-7g miRNA, suggesting that inhibition of let-7g miRNA is able to increase TLR4 mRNA. While parental PLC5 cells have a low susceptibility to LPS-induced cell growth, long-term LPS exposure for PLC5 cells leads to increased proliferation, cytokine expression and stemness properties. In conclusion, our studies demonstrate positive feedback regulation for chronic TLR4 activation in the modulation of TLR4 expression level through the LIN28A/let-7g pathway in HCC and suggest a connection between chronic inflammation and TLR4 expression level in HCC for promoting tumorigenesis.
Keywords: LIN28A; Toll-like receptors 4; hepatocellular carcinoma; let-7g.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

