A Review on the Molecular Mechanisms of Action of Natural Products in Preventing Bone Diseases
- PMID: 35955603
- PMCID: PMC9368769
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23158468
A Review on the Molecular Mechanisms of Action of Natural Products in Preventing Bone Diseases
Abstract
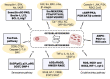
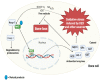
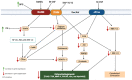
The drugs used for treating bone diseases (BDs), at present, elicit hazardous side effects that include certain types of cancers and strokes, hence the ongoing quest for the discovery of alternatives with little or no side effects. Natural products (NPs), mainly of plant origin, have shown compelling promise in the treatments of BDs, with little or no side effects. However, the paucity in knowledge of the mechanisms behind their activities on bone remodeling has remained a hindrance to NPs' adoption. This review discusses the pathological development of some BDs, the NP-targeted components, and the actions exerted on bone remodeling signaling pathways (e.g., Receptor Activator of Nuclear Factor κ B-ligand (RANKL)/monocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF)/osteoprotegerin (OPG), mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK)s/c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK)/nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB), Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 (Keap-1)/nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2)/Heme Oxygenase-1 (HO-1), Bone Morphogenetic Protein 2 (BMP2)-Wnt/β-catenin, PhosphatidylInositol 3-Kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (Akt)/Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3 Beta (GSK3β), and other signaling pathways). Although majority of the studies on the osteoprotective properties of NPs against BDs were conducted ex vivo and mostly on animals, the use of NPs for treating human BDs and the prospects for future development remain promising.
Keywords: bioactive compounds; bone diseases; bone remodeling; bone signaling pathways; natural products; osteoprotective properties.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Nrf2 deficiency induces oxidative stress and promotes RANKL-induced osteoclast differentiation.Free Radic Biol Med. 2013 Dec;65:789-799. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2013.08.005. Epub 2013 Aug 14. Free Radic Biol Med. 2013. PMID: 23954472
-
Caffeic acid 3,4-dihydroxy-phenethyl ester suppresses receptor activator of NF-κB ligand–induced osteoclastogenesis and prevents ovariectomy-induced bone loss through inhibition of mitogen-activated protein kinase/activator protein 1 and Ca2+–nuclear factor of activated T-cells cytoplasmic 1 signaling pathways.J Bone Miner Res. 2012 Jun;27(6):1298-1308. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.1576. J Bone Miner Res. 2012. PMID: 22337253
-
Quercetin disrupts tyrosine-phosphorylated phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and myeloid differentiation factor-88 association, and inhibits MAPK/AP-1 and IKK/NF-κB-induced inflammatory mediators production in RAW 264.7 cells.Immunobiology. 2013 Dec;218(12):1452-67. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2013.04.019. Epub 2013 May 9. Immunobiology. 2013. PMID: 23735482
-
Activation of Nrf2/HO-1 signaling: An important molecular mechanism of herbal medicine in the treatment of atherosclerosis via the protection of vascular endothelial cells from oxidative stress.J Adv Res. 2021 Jul 6;34:43-63. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2021.06.023. eCollection 2021 Dec. J Adv Res. 2021. PMID: 35024180 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Natural products for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases.Phytomedicine. 2023 Dec;121:155101. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155101. Epub 2023 Sep 18. Phytomedicine. 2023. PMID: 37778246 Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of the antibacterial effect of Epigallocatechin gallate on the major pathogens of canine periodontal disease and therapeutic effects on periodontal disease mice.Front Microbiol. 2024 Jan 5;14:1329772. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1329772. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38249491 Free PMC article.
-
Vitamin D Alleviates Heavy Metal-Induced Cytotoxic Effects on Human Bone Osteoblasts Via the Induction of Bioenergetic Disruption, Oxidative Stress, and Apoptosis.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2025 Apr;203(4):2420-2434. doi: 10.1007/s12011-024-04337-8. Epub 2024 Sep 5. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2025. PMID: 39235540 Free PMC article.
-
The role of the PKCζ/JNK signaling pathway in regulating the development of femoral head necrosis.Braz J Med Biol Res. 2025 Mar 3;58:e13771. doi: 10.1590/1414-431X2025e13771. eCollection 2025. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2025. PMID: 40053032 Free PMC article.
-
Differential Expression of Non-Coding RNAs in Stem Cell Development and Therapeutics of Bone Disorders.Cells. 2023 Apr 14;12(8):1159. doi: 10.3390/cells12081159. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37190068 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate on Bone Quality beyond Bone Density-A Scoping Review of the Literature.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Jan 23;17(2):146. doi: 10.3390/ph17020146. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38399361 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

