Kidney Injuries and Evolution of Chronic Kidney Diseases Due to Neonatal Hyperoxia Exposure Based on Animal Studies
- PMID: 35955627
- PMCID: PMC9369080
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23158492
Kidney Injuries and Evolution of Chronic Kidney Diseases Due to Neonatal Hyperoxia Exposure Based on Animal Studies
Abstract
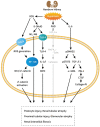
Preterm birth interrupts the development and maturation of the kidneys during the critical growth period. The kidneys can also exhibit structural defects and functional impairment due to hyperoxia, as demonstrated by various animal studies. Furthermore, hyperoxia during nephrogenesis impairs renal tubular development and induces glomerular and tubular injuries, which manifest as renal corpuscle enlargement, renal tubular necrosis, interstitial inflammation, and kidney fibrosis. Preterm birth along with hyperoxia exposure induces a pathological predisposition to chronic kidney disease. Hyperoxia-induced kidney injuries are influenced by several molecular factors, including hypoxia-inducible factor-1α and interleukin-6/Smad2/transforming growth factor-β, and Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathways; these are key to cell proliferation, tissue inflammation, and cell membrane repair. Hyperoxia-induced oxidative stress is characterized by the attenuation or the induction of multiple molecular factors associated with kidney damage. This review focuses on the molecular pathways involved in the pathogenesis of hyperoxia-induced kidney injuries to establish a framework for potential interventions.
Keywords: chronic kidney disease; hyperoxia; kidney fibrosis; kidney injury; nephrogenesis; prematurity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest regarding to this review article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
IL-6/Smad2 signaling mediates acute kidney injury and regeneration in a murine model of neonatal hyperoxia.FASEB J. 2019 May;33(5):5887-5902. doi: 10.1096/fj.201801875RR. Epub 2019 Feb 5. FASEB J. 2019. PMID: 30721632
-
Proximal Tubular Development Is Impaired with Downregulation of MAPK/ERK Signaling, HIF-1α, and Catalase by Hyperoxia Exposure in Neonatal Rats.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019 Aug 28;2019:9219847. doi: 10.1155/2019/9219847. eCollection 2019. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019. PMID: 31558952 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Klotho supplementation on hyperoxia-induced renal injury in a rodent model of postnatal nephrogenesis.Pediatr Res. 2020 Oct;88(4):565-570. doi: 10.1038/s41390-020-0803-z. Epub 2020 Feb 14. Pediatr Res. 2020. PMID: 32059229 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Preterm Birth on Renal Development and Renal Health Outcome.Neoreviews. 2019 Dec;20(12):e725-e736. doi: 10.1542/neo.20-12-e725. Neoreviews. 2019. PMID: 31792159 Review.
-
The Mechanism of Hyperoxia-Induced Neonatal Renal Injury and the Possible Protective Effect of Resveratrol.Am J Perinatol. 2024 Jul;41(9):1126-1133. doi: 10.1055/a-1817-5357. Epub 2022 Apr 5. Am J Perinatol. 2024. PMID: 35381611 Review.
Cited by
-
Oxygen Variations-Insights into Hypoxia, Hyperoxia and Hyperbaric Hyperoxia-Is the Dose the Clue?Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 30;24(17):13472. doi: 10.3390/ijms241713472. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37686277 Free PMC article.
-
The intelligent podocyte: sensing and responding to a complex microenvironment.Nat Rev Nephrol. 2025 Jul;21(7):503-516. doi: 10.1038/s41581-025-00965-y. Epub 2025 May 8. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 40341763 Review.
References
-
- Martin C.R., Brown Y.F., Ehrenkranz R.A., O’Shea T.M., Allred E.N., Belfort M.B., McCormick M.C., Leviton A. Extremely Low Gestational Age Newborns Study Investigators. Nutritional practices and growth velocity in the first month of life in extremely premature infants. Pediatrics. 2009;2:649–657. doi: 10.1542/peds.2008-3258. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

