Effects of Suramin on Polycystic Kidney Disease in a Mouse Model of Polycystin-1 Deficiency
- PMID: 35955634
- PMCID: PMC9369130
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23158499
Effects of Suramin on Polycystic Kidney Disease in a Mouse Model of Polycystin-1 Deficiency
Abstract
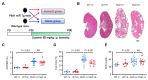
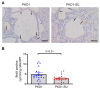
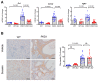
The aberrant activation of the purinergic signaling pathway has been shown to promote cyst growth and fluid secretion in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD). Suramin is an anti-parasitic drug that has strong anti-purinergic properties. Whether suramin could have a therapeutic effect on ADPKD has not been fully investigated. We examined the effect of suramin on cyst progression in a Pkd1 microRNAs transgenic mouse model that presented stable Pkd1 knockdown and moderate disease progression. The Pkd1-deficient mice were treated with suramin (60 mg/kg) by intraperitoneal injection twice a week from postnatal days 35 to 90. Kidney-to-body weight ratios, cyst indices, and blood urea nitrogen (BUN) levels were measured. Cell proliferation and macrophage infiltration were determined by immunohistochemistry. The suramin-treated group had significantly lower renal cyst densities, cell proliferation, and macrophage infiltration compared with saline-treated controls. Suramin significantly inhibited ERK phosphorylation and the expression of Il1b, Il6, Nlrp3, Tgfb, Fn1, P2rx7, and P2ry2 mRNAs in the kidneys. However, BUN levels remained high despite the reduction in cyst growth. Furthermore, plasma cystatin C and neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) levels were significantly higher in the suramin-treated group compared with the control group. Periodic acid-Schiff staining revealed degenerative changes and epithelial cell vacuolation in the non-cystic renal tubules, which indicated phospholipidosis following suramin treatment. These results suggest that suramin may reduce renal cyst growth and inflammation, but the associated tubular cell injuries could limit its therapeutic potential. Other purinergic receptor antagonists with less nephrotoxicity may deserve further investigation for the treatment of ADPKD.
Keywords: polycystic kidney disease; purinergic signaling; suramin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Ouabain enhances renal cyst growth in a slowly progressive mouse model of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2023 Dec 1;325(6):F857-F869. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00056.2023. Epub 2023 Oct 12. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2023. PMID: 37823195 Free PMC article.
-
Metformin induces lactate accumulation and accelerates renal cyst progression in Pkd1-deficient mice.Hum Mol Genet. 2022 May 19;31(10):1560-1573. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddab340. Hum Mol Genet. 2022. PMID: 34957500
-
Metformin improves relevant disease parameters in an autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease mouse model.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2022 Jan 1;322(1):F27-F41. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00298.2021. Epub 2021 Nov 22. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2022. PMID: 34806449
-
Polycystic kidney disease: novel insights into polycystin function.Trends Mol Med. 2023 Apr;29(4):268-281. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2023.01.005. Epub 2023 Feb 15. Trends Mol Med. 2023. PMID: 36805211 Review.
-
Cell Proliferation and Apoptosis in ADPKD.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016;933:25-34. doi: 10.1007/978-981-10-2041-4_3. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016. PMID: 27730432 Review.
Cited by
-
Transforming advancing autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease care: investigating new horizons in treatment and research.Inflammopharmacology. 2025 Aug 14. doi: 10.1007/s10787-025-01894-9. Online ahead of print. Inflammopharmacology. 2025. PMID: 40813527 Review.
-
Lysosomal Enhancement Prevents Infection with PrPSc, α-Synuclein & Tau Prions.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Aug 5:2025.06.24.661349. doi: 10.1101/2025.06.24.661349. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40667233 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Multiscale and multimodal evaluation of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease development.Commun Biol. 2024 Sep 19;7(1):1183. doi: 10.1038/s42003-024-06868-1. Commun Biol. 2024. PMID: 39300231 Free PMC article.
-
P2Y2R and Cyst Growth in Polycystic Kidney Disease.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2024 Oct 1;35(10):1351-1365. doi: 10.1681/ASN.0000000000000416. Epub 2024 Jun 7. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 38848134
-
The NLRP3 inflammasome in urogenital cancers: structure, dual function, and therapeutic potential.Front Oncol. 2025 Jul 11;15:1593774. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1593774. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40718836 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Olsan E.E., Mukherjee S., Wulkersdorfer B., Shillingford J.M., Giovannone A.J., Todorov G., Song X., Pei Y., Weimbs T. Signal transducer and activator of transcription-6 (STAT6) inhibition suppresses renal cyst growth in polycystic kidney disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2011;108:18067–18072. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1111966108. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

