Metabolic Remodeling with Hepatosteatosis Induced Vascular Oxidative Stress in Hepatic ERK2 Deficiency Mice with High Fat Diets
- PMID: 35955653
- PMCID: PMC9369278
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23158521
Metabolic Remodeling with Hepatosteatosis Induced Vascular Oxidative Stress in Hepatic ERK2 Deficiency Mice with High Fat Diets
Abstract
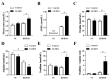
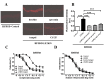
We previously demonstrated the marked hepatosteatosis and endothelial dysfunction in hepatocyte-specific ERK2 knockout mice (LE2KO) with a high-fat/high-sucrose diet (HFHSD), but detailed metabolic changes and the characteristics in insulin-sensitive organs were not tested. This study aimed to characterize metabolic remodeling with changes in insulin-sensitive organs, which could induce endothelial dysfunction in HFHSD-LE2KO. The serum glucose and fatty acid (FA) were modestly higher in HFHSD-LE2KO than HFHSD-Control. FA synthesis genes were up-regulated, which was associated with the decreased phosphorylation of AMPK and ACC, and with the up-regulation of SREBP-1 in the liver from HFHSD-LE2KO. In FA and amino acids fraction analysis, arachidonic acid/eicosapentaenoic acid ratio, L-ornithine/arginine ratio, asymmetric dimethylarginine and homocysteine levels were elevated in HFHSD-LE2KO. Insulin-induced phosphorylation of AKT was blunted in skeletal muscle. Serum leptin and IL-1β were elevated, and serum adiponectin was decreased with the enlargement of epididymal adipocytes. Finally, the enhanced superoxide levels in the aorta, which were blunted with CCCP, apocynin, and tempol, were observed in HFHSD-LE2KO. A pre-incubation of aortic rings with tempol improved endothelial dysfunction in HFHSD-LE2KO. HFHSD-LE2KO revealed an acceleration of FA synthesis in the liver leading to insulin resistance in skeletal muscle and the enlargement of visceral adipocytes. Global metabolic remodeling such as changes in arginine metabolism, ω3/ω6 ratio, and adipocytokines, could affect the vascular oxidative stress and endothelial dysfunction in HFHSD-LE2KO.
Keywords: ERK2; endothelial dysfunction; hepatosteatosis; insulin resistance; metabolic syndrome; metabolism.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Toh J.Z.K., Pan X.H., Tay P.W.L., Ng C.H., Yong J.N., Xiao J., Koh J.H., Tan E.Y., Tan E.X.X., Dan Y.Y., et al. A Meta-Analysis on the Global Prevalence, Risk factors and Screening of Coronary Heart Disease in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021 doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2021.09.021. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

