Metabolic Effects of the Waist-To-Hip Ratio Associated Locus GRB14/COBLL1 Are Related to GRB14 Expression in Adipose Tissue
- PMID: 35955692
- PMCID: PMC9369072
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23158558
Metabolic Effects of the Waist-To-Hip Ratio Associated Locus GRB14/COBLL1 Are Related to GRB14 Expression in Adipose Tissue
Abstract
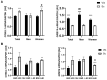
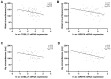
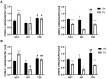
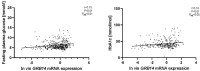
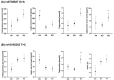
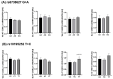
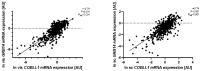
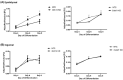
GRB14/COBLL1 locus has been shown to be associated with body fat distribution (FD), but neither the causal gene nor its role in metabolic diseases has been elucidated. We hypothesize that GRB14/COBLL1 may act as the causal genes for FD-related SNPs (rs10195252 and rs6738627), and that they may be regulated by SNP to effect obesity-related metabolic traits. We genotyped rs10195252 and rs6738627 in 2860 subjects with metabolic phenotypes. In a subgroup of 560 subjects, we analyzed GRB14/COBLL1 gene expression in paired visceral and subcutaneous adipose tissue (AT) samples. Mediation analyses were used to determine the causal relationship between SNPs, AT GRB14/COBLL1 mRNA expression, and obesity-related traits. In vitro gene knockdown of Grb14/Cobll1 was used to test their role in adipogenesis. Both gene expressions in AT are correlated with waist circumference. Visceral GRB14 mRNA expression is associated with FPG and HbA1c. Both SNPs are associated with triglycerides, FPG, and leptin levels. Rs10195252 is associated with HbA1c and seems to be mediated by visceral AT GRB14 mRNA expression. Our data support the role of the GRB14/COBLL1 gene expression in body FD and its locus in metabolic sequelae: in particular, lipid metabolism and glucose homeostasis, which is likely mediated by AT GRB14 transcript levels.
Keywords: COBLL1; GRB14; adipose tissue; rs10195252; rs6738627.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Khera A.V., Chaffin M., Aragam K.G., Haas M.E., Roselli C., Choi S.H., Natarajan P., Lander E.S., Lubitz S.A., Ellinor P.T., et al. Genome-wide polygenic scores for common diseases identify individuals with risk equivalent to monogenic mutations. Nat. Genet. 2018;50:1219–1224. doi: 10.1038/s41588-018-0183-z. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

