The Role of PKC-MAPK Signalling Pathways in the Development of Hyperglycemia-Induced Cardiovascular Complications
- PMID: 35955714
- PMCID: PMC9369123
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23158582
The Role of PKC-MAPK Signalling Pathways in the Development of Hyperglycemia-Induced Cardiovascular Complications
Abstract
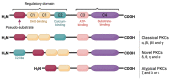
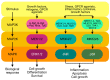
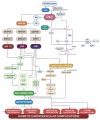
Cardiovascular disease is the most common cause of death among diabetic patients worldwide. Hence, cardiovascular wellbeing in diabetic patients requires utmost importance in disease management. Recent studies have demonstrated that protein kinase C activation plays a vital role in the development of cardiovascular complications via its activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) cascades, also known as PKC-MAPK pathways. In fact, persistent hyperglycaemia in diabetic conditions contribute to preserved PKC activation mediated by excessive production of diacylglycerol (DAG) and oxidative stress. PKC-MAPK pathways are involved in several cellular responses, including enhancing oxidative stress and activating signalling pathways that lead to uncontrolled cardiac and vascular remodelling and their subsequent dysfunction. In this review, we discuss the recent discovery on the role of PKC-MAPK pathways, the mechanisms involved in the development and progression of diabetic cardiovascular complications, and their potential as therapeutic targets for cardiovascular management in diabetic patients.
Keywords: ERK1/2; JNK; cardiac remodelling; p38; vascular dysfunction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funder had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Role of ERK1/2 in the Development of Diabetic Cardiomyopathy.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Dec 8;17(12):2001. doi: 10.3390/ijms17122001. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27941647 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of MAP kinase-mediated endothelial dysfunction in hyperglycemia via arginase I and eNOS dysregulation.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2019 Sep;1866(9):1398-1411. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2019.05.004. Epub 2019 May 28. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2019. PMID: 31150695
-
The role of protein kinase C activation and the vascular complications of diabetes.Pharmacol Res. 2007 Jun;55(6):498-510. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2007.04.016. Epub 2007 May 5. Pharmacol Res. 2007. PMID: 17574431 Review.
-
Amelioration of hyperglycemic and hyperosmotic induced vascular dysfunction by in vivo inhibition of protein kinase C and p38 MAP kinase pathway in the rat mesenteric microcirculation.Eur J Clin Invest. 2000 Jul;30(7):586-93. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2362.2000.00680.x. Eur J Clin Invest. 2000. PMID: 10886298
-
Chronic exposure of human mesangial cells to high glucose environments activates the p38 MAPK pathway.Kidney Int. 2001 Sep;60(3):858-71. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1755.2001.060003858.x. Kidney Int. 2001. PMID: 11532081
Cited by
-
Exploring early DNA methylation alterations in type 1 diabetes: implications of glycemic control.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Jun 5;15:1416433. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1416433. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38904047 Free PMC article.
-
Key Therapeutic Targets to Treat Hyperglycemia-Induced Atherosclerosis Analyzed Using a Petri Net-Based Model.Metabolites. 2023 Dec 8;13(12):1191. doi: 10.3390/metabo13121191. Metabolites. 2023. PMID: 38132873 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of Oxidative Stress in Metabolic Syndrome.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 26;24(9):7898. doi: 10.3390/ijms24097898. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37175603 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Significance of MAPK Signaling Pathway in the Diagnosis and Subtype Classification of Intervertebral Disc Degeneration.JOR Spine. 2025 Mar 24;8(1):e70060. doi: 10.1002/jsp2.70060. eCollection 2025 Mar. JOR Spine. 2025. PMID: 40134951 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances in Pyrazole-based Protein Kinase Inhibitors as Emerging Therapeutic Targets.Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2024;27(19):2791-2804. doi: 10.2174/0113862073252211231024182817. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2024. PMID: 37946345 Review.
References
-
- Federation I.D. IDF Diabetes Atlas. 10th ed. International Diabetes Federation; Brussel, Belgium: 2021.
-
- Ambady R., Chamukuttan S., Nanditha A. Classification and Diagnosis of Diabetes. In: Holt R.I.G., Cockram C.S., Flyvbjerg A., Goldstein B.J., editors. Classification and Diagnosis of Diabetes. Wiley-Blackwell Publishing Ltd; Chichester, UK: 2017. pp. 23–28.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

