p-Coumaric acid, Kaempferol, Astragalin and Tiliroside Influence the Expression of Glycoforms in AGS Gastric Cancer Cells
- PMID: 35955735
- PMCID: PMC9369150
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23158602
p-Coumaric acid, Kaempferol, Astragalin and Tiliroside Influence the Expression of Glycoforms in AGS Gastric Cancer Cells
Abstract
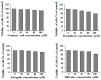
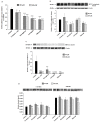
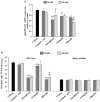
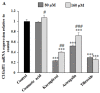
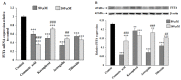
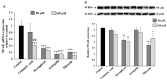
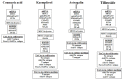
Abnormal glycosylation of cancer cells is considered a key factor of carcinogenesis related to growth, proliferation, migration and invasion of tumor cells. Many plant-based polyphenolic compounds reveal potential anti-cancer properties effecting cellular signaling systems. Herein, we assessed the effects of phenolic acid, p-coumaric acid and flavonoids such as kaempferol, astragalin or tiliroside on expression of selected cancer-related glycoforms and enzymes involved in their formation in AGS gastric cancer cells. The cells were treated with 80 and 160 µM of the compounds. RT-PCR, Western blotting and ELISA tests were performed to determine the influence of polyphenolics on analyzed factors. All the examined compounds inhibited the expression of MUC1, ST6GalNAcT2 and FUT4 mRNAs. C1GalT1, St3Gal-IV and FUT4 proteins as well as MUC1 domain, Tn and sialyl T antigen detected in cell lysates were also lowered. Both concentrations of kaempferol, astragalin and tiliroside also suppressed ppGalNAcT2 and C1GalT1 mRNAs. MUC1 cytoplasmic domain, sialyl Tn, T antigens in cell lysates and sialyl T in culture medium were inhibited only by kaempferol and tiliroside. Nuclear factor NF-κB mRNA expression decreased after treatment with both concentrations of kaempferol, astragalin and tiliroside. NF-κB protein expression was inhibited by kaempferol and tiliroside. The results indicate the rationality of application of examined polyphenolics as potential preventive agents against gastric cancer development.
Keywords: MUC1; gastric cancer; glycosylation; polyphenolics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures




References
-
- Maiuolo J., Musolino V., Gliozzi M., Carresi C., Oppedisano F., Nucera S., Scarano F., Scicchitano M., Guarnieri L., Bosco F., et al. The employment of genera Vaccinium, Citrus, Olea, and Cynara polyphenols for the reduction of selected anti-cancer drug side effects. Nutrients. 2022;14:1574. doi: 10.3390/nu14081574. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

