Evaluation of Orbital Lymphoproliferative and Inflammatory Disorders by Gene Expression Analysis
- PMID: 35955742
- PMCID: PMC9369106
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23158609
Evaluation of Orbital Lymphoproliferative and Inflammatory Disorders by Gene Expression Analysis
Abstract
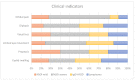
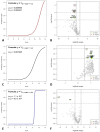
Non-specific orbital inflammation (NSOI) and IgG4-related orbital disease (IgG4-ROD) are often challenging to differentiate. Furthermore, it is still uncertain how chronic inflammation, such as IgG4-ROD, can lead to mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) lymphoma. Therefore, we aimed to evaluate the diagnostic value of gene expression analysis to differentiate orbital autoimmune diseases and elucidate genetic overlaps. First, we established a database of NSOI, relapsing NSOI, IgG4-ROD and MALT lymphoma patients of our orbital center (2000−2019). In a consensus process, three typical patients of the above mentioned three groups (mean age 56.4 ± 17 years) at similar locations were selected. Afterwards, RNA was isolated using the RNeasy FFPE kit (Qiagen) from archived paraffin-embedded tissues. The RNA of these 12 patients were then subjected to gene expression analysis (NanoString nCounter®), including a total of 1364 target genes. The most significantly upregulated and downregulated genes were used for a machine learning algorithm to distinguish entities. This was possible with a high probability (p < 0.0001). Interestingly, gene expression patterns showed a characteristic overlap of lymphoma with IgG4-ROD and NSOI. In contrast, IgG4-ROD shared only altered expression of one gene regarding NSOI. To validate our potential biomarker genes, we isolated the RNA of a further 48 patients (24 NSOI, 11 IgG4-ROD, 13 lymphoma patients). Then, gene expression pattern analysis of the 35 identified target genes was performed using a custom-designed CodeSet to assess the prediction accuracy of the multi-parameter scoring algorithms. They showed high accuracy and good performance (AUC ROC: IgG4-ROD 0.81, MALT 0.82, NSOI 0.67). To conclude, genetic expression analysis has the potential for faster and more secure differentiation between NSOI and IgG4-ROD. MALT-lymphoma and IgG4-ROD showed more genetic similarities, which points towards progression to lymphoma.
Keywords: IgG4-ROD; IgG4-related orbitopathy; MALT; idiopathic orbital inflammation; lymphoma; non-specific orbital inflammation; pseudotumor orbitae.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Novel Insights into Pathophysiology of Orbital Inflammatory Diseases and Progression to Orbital Lymphoma by Pathway Enrichment Analysis.Life (Basel). 2022 Oct 20;12(10):1660. doi: 10.3390/life12101660. Life (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36295095 Free PMC article.
-
Differential Tissue Metabolic Signatures in IgG4-Related Ophthalmic Disease and Orbital Mucosa-Associated Lymphoid Tissue Lymphoma.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2021 Jan 4;62(1):15. doi: 10.1167/iovs.62.1.15. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2021. PMID: 33439228 Free PMC article.
-
Immunophenotypic profiles for distinguishing orbital mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma from benign lymphoproliferative tumors.Jpn J Ophthalmol. 2017 Jul;61(4):354-360. doi: 10.1007/s10384-017-0513-1. Epub 2017 Apr 18. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 2017. PMID: 28421369
-
Non-specific orbital inflammation: Current understanding and unmet needs.Prog Retin Eye Res. 2021 Mar;81:100885. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2020.100885. Epub 2020 Jul 24. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2021. PMID: 32717379 Review.
-
Characteristics, diagnosis and therapeutic strategies for IgG4-related orbital disease.Pharmacol Rep. 2016 Jun;68(3):507-13. doi: 10.1016/j.pharep.2015.11.011. Epub 2015 Dec 22. Pharmacol Rep. 2016. PMID: 27116895 Review.
Cited by
-
Elucidating the multifaceted roles of GPR146 in non-specific orbital inflammation: a concerted analytical approach through the prisms of bioinformatics and machine learning.Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 Jun 5;11:1309510. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1309510. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38903815 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated multiple machine learning and Mendelian randomization reveal LTF gene as a prognostic biomarker for nonspecific orbital inflammation.BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2025 Aug 4;26(1):143. doi: 10.1186/s40360-025-00980-6. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2025. PMID: 40760708 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Insights into Pathophysiology of Orbital Inflammatory Diseases and Progression to Orbital Lymphoma by Pathway Enrichment Analysis.Life (Basel). 2022 Oct 20;12(10):1660. doi: 10.3390/life12101660. Life (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36295095 Free PMC article.
-
Glutamine metabolism-related genes and immunotherapy in nonspecific orbital inflammation were validated using bioinformatics and machine learning.BMC Genomics. 2024 Jan 17;25(1):71. doi: 10.1186/s12864-023-09946-6. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 38233749 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering the role of HLF in idiopathic orbital inflammation: integrative analysis via bioinformatics and machine learning techniques.Sci Rep. 2024 Aug 20;14(1):19346. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-68890-x. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39164324 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

