Screening and Verification of Photosynthesis and Chloroplast-Related Genes in Mulberry by Comparative RNA-Seq and Virus-Induced Gene Silencing
- PMID: 35955752
- PMCID: PMC9368790
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23158620
Screening and Verification of Photosynthesis and Chloroplast-Related Genes in Mulberry by Comparative RNA-Seq and Virus-Induced Gene Silencing
Abstract
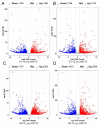
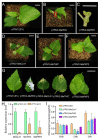
Photosynthesis is one of the most important factors in mulberry growth and production. To study the photosynthetic regulatory network of mulberry we sequenced the transcriptomes of two high-yielding (E1 and E2) and one low-yielding (H32) mulberry genotypes at two-time points (10:00 and 12:00). Re-annotation of the mulberry genome based on the transcriptome sequencing data identified 22,664 high-quality protein-coding genes with a BUSCO-assessed completeness of 93.4%. A total of 6587 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were obtained in the transcriptome analysis. Functional annotation and enrichment revealed 142 out of 6587 genes involved in the photosynthetic pathway and chloroplast development. Moreover, 3 out of 142 genes were further examined using the VIGS technique; the leaves of MaCLA1- and MaTHIC-silenced plants were markedly yellowed or even white, and the leaves of MaPKP2-silenced plants showed a wrinkled appearance. The expression levels of the ensiled plants were reduced, and the levels of chlorophyll b and total chlorophyll were lower than those of the control plants. Co-expression analysis showed that MaCLA1 was co-expressed with CHUP1 and YSL3; MaTHIC was co-expressed with MaHSP70, MaFLN1, and MaEMB2794; MaPKP2 was mainly co-expressed with GH9B7, GH3.1, and EDA9. Protein interaction network prediction revealed that MaCLA1 was associated with RPE, TRA2, GPS1, and DXR proteins; MaTHIC was associated with TH1, PUR5, BIO2, and THI1; MaPKP2 was associated with ENOC, LOS2, and PGI1. This study offers a useful resource for further investigation of the molecular mechanisms involved in mulberry photosynthesis and preliminary insight into the regulatory network of photosynthesis.
Keywords: VIGS; mulberry; photosynthesis regulation; re-annotation; transcriptomes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Gan T., Lin Z., Bao L., Hui T., Cui X., Huang Y., Wang H., Su C., Jiao F., Zhang M., et al. Comparative Proteomic Analysis of Tolerant and Sensitive Varieties Reveals That Phenylpropanoid Biosynthesis Contributes to Salt Tolerance in Mulberry. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021;22:9402. doi: 10.3390/ijms22179402. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zafar Z., Rasheed F., Ul Haq A., Ibrahim F.H., Afzal S., Nazre M., Akram S., Hussain Z., Kudus K.A., Mohsin M., et al. Interspecific Differences in Physiological and Biochemical Traits Drive the Water Stress Tolerance in Young Morus alba L. and Conocarpus erectus L. Saplings. Plants. 2021;10:1615. doi: 10.3390/plants10081615. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

