Further Evidence of Neuroprotective Effects of Recombinant Human Erythropoietin and Growth Hormone in Hypoxic Brain Injury in Neonatal Mice
- PMID: 35955834
- PMCID: PMC9368903
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23158693
Further Evidence of Neuroprotective Effects of Recombinant Human Erythropoietin and Growth Hormone in Hypoxic Brain Injury in Neonatal Mice
Abstract
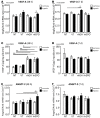
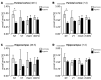
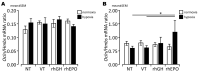
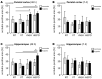
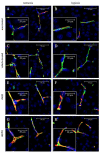
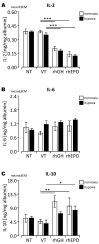
Experimental in vivo data have recently shown complementary neuroprotective actions of rhEPO and growth hormone (rhGH) in a neonatal murine model of hypoxic brain injury. Here, we hypothesized that rhGH and rhEPO mediate stabilization of the blood−brain barrier (BBB) and regenerative vascular effects in hypoxic injury to the developing brain. Using an established model of neonatal hypoxia, neonatal mice (P7) were treated i.p. with rhGH (4000 µg/kg) or rhEPO (5000 IU/kg) 0/12/24 h after hypoxic exposure. After a regeneration period of 48 h or 7 d, cerebral mRNA expression of Vegf-A, its receptors and co-receptors, and selected tight junction proteins were determined using qRT-PCR and ELISA. Vessel structures were assessed by Pecam-1 and occludin (Ocln) IHC. While Vegf-A expression increased significantly with rhGH treatment (p < 0.01), expression of the Vegfr and TEK receptor tyrosine kinase (Tie-2) system remained unchanged. RhEPO increased Vegf-A (p < 0.05) and Angpt-2 (p < 0.05) expression. While hypoxia reduced the mean vessel area in the parietal cortex compared to controls (p < 0.05), rhGH and rhEPO prevented this reduction after 48 h of regeneration. Hypoxia significantly reduced the Ocln+ fraction of cortical vascular endothelial cells. Ocln signal intensity increased in the cortex in response to rhGH (p < 0.05) and in the cortex and hippocampus in response to rhEPO (p < 0.05). Our data indicate that rhGH and rhEPO have protective effects on hypoxia-induced BBB disruption and regenerative vascular effects during the post-hypoxic period in the developing brain.
Keywords: VEGF-A; angiogenesis; angiopoietins; blood–brain barrier; hypoxia; hypoxic brain injury; neurovascular unit; occludin; tight junction proteins; vasculogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Cainelli E., Vedovelli L., Mastretta E., Gregori D., Suppiej A., Bisiacchi P.S. Long-Term Outcomes after Neonatal Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy in the Era of Therapeutic Hypothermia: A Longitudinal, Prospective, Multicenter Case-Control Study in Children without Overt Brain Damage. Children. 2021;8:1076. doi: 10.3390/children8111076. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Trollmann R., Mühlberger T., Richter M., Boie G., Feigenspan A., Brackmann F., Jung S. Differential regulation of angiogenesis in the developing mouse brain in response to exogenous activation of the hypoxia-inducible transcription factor system. Brain Res. 2018;1688:91–102. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2018.03.012. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

