Regulatory T Cell Depletion Using a CRISPR Fc-Optimized CD25 Antibody
- PMID: 35955841
- PMCID: PMC9369266
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23158707
Regulatory T Cell Depletion Using a CRISPR Fc-Optimized CD25 Antibody
Abstract
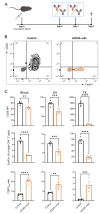
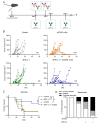
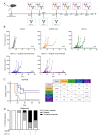
Regulatory T cells (Tregs) are major drivers behind immunosuppressive mechanisms and present a major hurdle for cancer therapy. Tregs are characterized by a high expression of CD25, which is a potentially valuable target for Treg depletion to alleviate immune suppression. The preclinical anti-CD25 (αCD25) antibody, clone PC-61, has met with modest anti-tumor activity due to its capacity to clear Tregs from the circulation and lymph nodes, but not those that reside in the tumor. The optimization of the Fc domain of this antibody clone has been shown to enhance the intratumoral Treg depletion capacity. Here, we generated a stable cell line that produced optimized recombinant Treg-depleting antibodies. A genome engineering strategy in which CRISPR-Cas9 was combined with homology-directed repair (CRISPR-HDR) was utilized to optimize the Fc domain of the hybridoma PC-61 for effector functions by switching it from its original rat IgG1 to a mouse IgG2a isotype. In a syngeneic tumor mouse model, the resulting αCD25-m2a (mouse IgG2a isotype) antibody mediated the effective depletion of tumor-resident Tregs, leading to a high effector T cell (Teff) to Treg ratio. Moreover, a combination of αCD25-m2a and an αPD-L1 treatment augmented tumor eradication in mice, demonstrating the potential for αCD25 as a cancer immunotherapy.
Keywords: CRISPR-HDR; Fc optimization; antibody; hybridoma; immunotherapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Jones E., Dahm-Vicker M., Simon A.K., Green A., Powrie F., Cerundolo V., Gallimore A. Depletion of CD25+ Regulatory Cells Results in Suppression of Melanoma Growth and Induction of Autoreactivity in Mice-PubMed. Cancer Immun. 2002;2:1. - PubMed
-
- Hodi F.S., Butler M., Oble D.A., Seiden M.V., Haluska F.G., Kruse A., MacRae S., Nelson M., Canning C., Lowy I., et al. Immunologic and Clinical Effects of Antibody Blockade of Cytotoxic T Lymphocyte-Associated Antigen 4 in Previously Vaccinated Cancer Patients. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2008;105:3005–3010. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0712237105. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

