Mechanisms of Systemic Osteoporosis in Rheumatoid Arthritis
- PMID: 35955873
- PMCID: PMC9368786
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23158740
Mechanisms of Systemic Osteoporosis in Rheumatoid Arthritis
Abstract
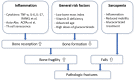
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA), an autoimmune disease, is characterized by the presence of symmetric polyarthritis predominantly of the small joints that leads to severe cartilage and bone destruction. Based on animal and human data, the pathophysiology of osteoporosis, a frequent comorbidity in conjunction with RA, was delineated. Autoimmune inflammatory processes, which lead to a systemic upregulation of inflammatory and osteoclastogenic cytokines, the production of autoantibodies, and Th cell senescence with a presumed disability to control the systemic immune system's and osteoclastogenic status, may play important roles in the pathophysiology of osteoporosis in RA. Consequently, osteoclast activity increases, osteoblast function decreases and bone metabolic and mechanical properties deteriorate. Although a number of disease-modifying drugs to treat joint inflammation are available, data on the ability of these drugs to prevent fragility fractures are limited. Thus, specific treatment of osteoporosis should be considered in patients with RA and an associated increased risk of fragility fractures.
Keywords: bone mineral density; fractures; osteoporosis; pathophysiology; rheumatoid arthritis; sarcopenia.
Conflict of interest statement
Peter Pietschmann received research support and/or honoraria from Amgen GmbH, Biomedica GmbH, Fresenius Kabi Austria, Takeda Pharma GesmbH, TAmiRNA GmbH, UCB Biopharma Srl/UCB Pharma. Katharina Kerschan-Schindl has received research support and/or remuneration from Amgen GmbH, Lilly GmbH, Merck, Sharp and Dohme GmbH, Stada GmbH, Roche Austria, and Servier Austria. Maria Butylina and Wolfgang Sipos state that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- De Sire A., Invernizzi M., Baricich A., Lippi L., Ammendolia A., Grassi F.A., Leigheb M. Optimization of transdisciplinary management of elderly with femur proximal extremity fracture: A patient-tailored plan from orthopaedics to rehabilitation. World J. Orthop. 2021;12:456–466. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v12.i7.456. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

