Genome-Wide Identification of Brassicaceae Hormone-Related Transcription Factors and Their Roles in Stress Adaptation and Plant Height Regulation in Allotetraploid Rapeseed
- PMID: 35955899
- PMCID: PMC9369146
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23158762
Genome-Wide Identification of Brassicaceae Hormone-Related Transcription Factors and Their Roles in Stress Adaptation and Plant Height Regulation in Allotetraploid Rapeseed
Abstract
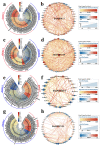
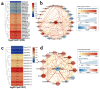
Phytohormone-related transcription factors (TFs) are involved in regulating stress responses and plant growth. However, systematic analysis of these TFs in Brassicaceae is limited, and their functions in stress adaptation and plant height (PH) regulation remain unclear. In this study, 2115 hormone-related TFs were identified in nine Brassicaceae species. Specific domains were found in several Brassicaceae hormone-related TFs, which may be associated with diverse functions. Syntenic analysis indicated that expansion of these genes was mainly caused by segmental duplication, with whole-genome duplication occurring in some species. Differential expression analysis and gene co-expression network analysis identified seven phytohormone-related TFs (BnaWRKY7, 21, 32, 38, 52, BnaGL3-4, and BnaAREB2-5) as possible key genes for cadmium (Cd) toxicity, salinity stress, and potassium (K) and nitrogen (N) deficiencies. Furthermore, BnaWRKY42 and BnaARR21 may play essential roles in plant height. Weighted gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA) identified 15 phytohormone-related TFs and their potential target genes regulating stress adaptation and plant height. Among the above genes, BnaWRKY56 and BnaWRKY60 responded to four different stresses simultaneously, and BnaWRKY42 was identified in two dwarf rapeseeds. In summary, several candidate genes for stress resistance (BnaWRKY56 and BnaWRKY60) and plant height (BnaWRKY42) were identified. These findings should help elucidate the biological roles of Brassicaceae hormone-related TFs, and the identified candidate genes should provide a genetic resource for the potential development of stress-tolerant and dwarf oilseed plants.
Keywords: Brassicaceae; abiotic stress; phytohormone; plant height; transcription factors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures







References
-
- Okushima Y., Overvoorde P.J., Arima K., Alonso J.M., Chan A., Chang C., Ecker J.R., Hughes B., Lui A., Nguyen D., et al. Functional genomic analysis of the AUXIN RESPONSE FACTOR gene family members in Arabidopsis thaliana: Unique and overlapping functions of ARF7 and ARF19. Plant Cell. 2005;17:444–463. doi: 10.1105/tpc.104.028316. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2021M692944/Chinese Postdoctoral Science Foundation
- 32212399 and 32213006/Research Start-Up Project
- 22610002/Famous Teachers in Central Plains
- 202102110006/Application of Molecular Design Breeding of Oil Crops and Intelligent Auxiliary Information System in Supercomputing Ecology, Henan Key Project of Science and Technology
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

