Overexpression of the Arabidopsis MACPF Protein AtMACP2 Promotes Pathogen Resistance by Activating SA Signaling
- PMID: 35955922
- PMCID: PMC9369274
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23158784
Overexpression of the Arabidopsis MACPF Protein AtMACP2 Promotes Pathogen Resistance by Activating SA Signaling
Abstract
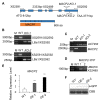
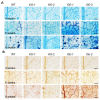
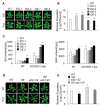
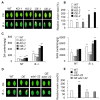
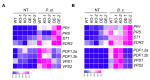
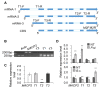
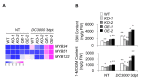
Immune response in plants is tightly regulated by the coordination of the cell surface and intracellular receptors. In animals, the membrane attack complex/perforin-like (MACPF) protein superfamily creates oligomeric pore structures on the cell surface during pathogen infection. However, the function and molecular mechanism of MACPF proteins in plant pathogen responses remain largely unclear. In this study, we identified an Arabidopsis MACP2 and investigated the responsiveness of this protein during both bacterial and fungal pathogens. We suggest that MACP2 induces programmed cell death, bacterial pathogen resistance, and necrotrophic fungal pathogen sensitivity by activating the biosynthesis of tryptophan-derived indole glucosinolates and the salicylic acid signaling pathway dependent on the activity of enhanced disease susceptibility 1 (EDS1). Moreover, the response of MACP2 mRNA isoforms upon pathogen attack is differentially regulated by a posttranscriptional mechanism: alternative splicing. In comparison to previously reported MACPFs in Arabidopsis, MACP2 shares a redundant but nonoverlapping role in plant immunity. Thus, our findings provide novel insights and genetic tools for the MACPF family in maintaining SA accumulation in response to pathogens in Arabidopsis.
Keywords: MACP2; indole glucosinolates; membrane attack complex/perforin-like protein; pathogen infection; salicylic acid signaling.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Fukunaga S., Sogame M., Hata M., Singkaravanit-Ogawa S., Pislewska-Bednarek M., Onozawa-Komori M., Nishiuchi T., Hiruma K., Saitoh H., Terauchi R., et al. Dysfunction of Arabidopsis MACPF domain protein activates programmed cell death via tryptophan metabolism in MAMP-triggered immunity. Plant J. 2017;89:381–393. doi: 10.1111/tpj.13391. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

