DNase-1 Treatment Exerts Protective Effects in Neurogenic Pulmonary Edema via Regulating the Neutrophil Extracellular Traps after Subarachnoid Hemorrhage in Mice
- PMID: 35955969
- PMCID: PMC9369252
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm11154349
DNase-1 Treatment Exerts Protective Effects in Neurogenic Pulmonary Edema via Regulating the Neutrophil Extracellular Traps after Subarachnoid Hemorrhage in Mice
Abstract
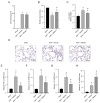
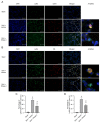
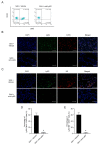
It has been reported that neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) involve inflammation, coagulation and cell death. Acute lung injury is also considered to be connected with NETs. Deoxyribonuclease I (DNase-1), a clinical medication for the respiratory system, has been reported to degrade cell-free DNA (cfDNA), which is the main component of NETs. Herein, we did research to clarify the therapeutic value of DNase-1 in NPE after SAH. In this model, we found that the treatment of DNase-1 remarkably decreased lung water, neutrophilic infiltration and inflammation. In addition, DNase-1 inhibited the NETs and proinflammatory subtype transition of the macrophages. Moreover, the depletion of neutrophil also verified the role of NETs in NPE. Our results suggest that DNase-1 has the potential to effectively relieve the NPE after SAH and to be a clinical drug for use after SAH.
Keywords: DNase-1; inflammation; neurogenic pulmonary edema; neutrophil extracellular traps; subarachnoid hemorrhage.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Neutrophil Extracellular Traps may be a Potential Target for Treating Early Brain Injury in Subarachnoid Hemorrhage.Transl Stroke Res. 2022 Feb;13(1):112-131. doi: 10.1007/s12975-021-00909-1. Epub 2021 Apr 14. Transl Stroke Res. 2022. PMID: 33852132
-
Neutrophil extracellular traps are associated with the pathogenesis of diffuse alveolar hemorrhage in murine lupus.J Autoimmun. 2019 Jun;100:120-130. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2019.03.009. Epub 2019 Mar 28. J Autoimmun. 2019. PMID: 30930069
-
Archaea-inspired deoxyribonuclease I liposomes prevent multiple organ dysfunction in sepsis.J Control Release. 2025 Apr 10;380:1109-1126. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2025.02.050. Epub 2025 Feb 26. J Control Release. 2025. PMID: 39986474
-
Neurogenic pulmonary edema in subarachnoid hemorrhage: relevant clinical concepts.Egypt J Neurosurg. 2021;36(1):27. doi: 10.1186/s41984-021-00124-y. Epub 2021 Nov 15. Egypt J Neurosurg. 2021. PMID: 34988372 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Progression of Cystic Fibrosis Lung Disease from Childhood to Adulthood: Neutrophils, Neutrophil Extracellular Trap (NET) Formation, and NET Degradation.Genes (Basel). 2019 Feb 26;10(3):183. doi: 10.3390/genes10030183. Genes (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30813645 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Neutrophil extracellular traps in homeostasis and disease.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024 Sep 20;9(1):235. doi: 10.1038/s41392-024-01933-x. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024. PMID: 39300084 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The neutrophil extracellular traps in neurological diseases: an update.Clin Exp Immunol. 2024 Nov 12;218(3):264-274. doi: 10.1093/cei/uxae057. Clin Exp Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38975702 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bederson J.B., Connolly E.S., Batjer H.H., Dacey R.G., Dion J.E., Diringer M., Duldner J.E., Harbaugh R., Patel A.B., Rosenwasser R.H. Guidelines for the management of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: A statement for healthcare professionals from a special writing group of the Stroke Council, American Heart Association. Stroke. 2009;40:994–1025. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.108.191395. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bruder N., The Participants in the International Multi-disciplinary Consensus Conference on the Critical Care Management of Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. Rabinstein A. Cardiovascular and pulmonary complications of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurocrit. Care. 2011;15:257–269. doi: 10.1007/s12028-011-9598-4. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

