Imaging Activated-T-Lymphocytes in the Salivary Glands of Patients with Sjögren's Syndrome by 99mTc-Interleukin-2: Diagnostic and Therapeutic Implications
- PMID: 35955984
- PMCID: PMC9369053
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm11154368
Imaging Activated-T-Lymphocytes in the Salivary Glands of Patients with Sjögren's Syndrome by 99mTc-Interleukin-2: Diagnostic and Therapeutic Implications
Abstract
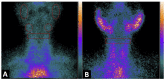
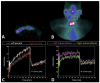
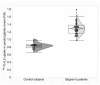
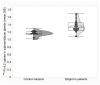
Background: Sjögren’s syndrome (SS) is a progressive autoimmune disease characterized by local mononuclear cell infiltration of the salivary and lachrymal glands. Labial biopsy demonstrates local infiltration by Th1 cells that produce pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as interleukin-2 (IL2). The aim of this study was to assess the utility of 99mTc-labelled-IL2 (99mTc-IL2) in evaluating in vivo the extent and severity of lympho-mononuclear cell infiltration in the salivary glands of patients with SS. Methods: We investigated 48 patients with primary SS and 27 control subjects using 99mTc-IL2 scintigraphy. Furthermore, in a subgroup of 30 patients, we also performed 99mTc-pertechnetate scintigraphy (99mTcO4−) for evaluation of the salivary gland function. Results: 99mTc-IL2 uptake in the salivary glands of SS patients was higher than in the control subjects (1.30 ± 0.16 vs. 0.83 ± 0.08 for parotids and 1.36 ± 0.15 vs. 1.16 ± 0.07 for submandibular glands; p < 0.0001). The salivary gland uptake of 99mTc-IL2 in patients with a longer history of disease was lower compared with the recently diagnosed patients. A significant direct correlation was found between the uptake of 99mTc-IL2 and histology. Conclusions: 99mTc-IL2 scintigraphy showed that the degree of lymphocytic infiltration of major salivary glands is variable in patients with different disease durations. Patients with a high 99mTc-IL2 uptake could be efficiently treated with immuno-modulatory drugs and the efficacy of treatment could be followed-up by 99mTc-IL2 scintigraphy.
Keywords: 99mTc-interleukin-2; Sjögren’s syndrome; activated lymphocytes; inflammation imaging; salivary glands.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Manthorpe R., Jacobsson L.T., Kirtava Z., Theander E. Epidemiology of Sjögren’s syndrome, especially its primary form. Ann. Med. Interne. 1998;149:7–11. - PubMed
-
- Vitali C., Moutsopoulos H.M., Bombardieri S. The European Community Study Group on diagnostic criteria for Sjogren’s syndrome. Sensitivity and specificity of tests for ocular and oral involvement in Sjogren’s syndrome. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 1994;53:637–647. doi: 10.1136/ard.53.10.637. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Vitali C., Bombardieri S., Jonsson R., Moutsopoulos H.M., Alexander E.L., Carsons S.E., Daniels T.E., Fox P.C., Fox R.I., Kassan S.S., et al. Classification criteria for Sjogren’s syndrome: A revised version of the European criteria proposed by the American-European Consensus Group. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2002;6:554–558. doi: 10.1136/ard.61.6.554. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

