Assessment of Renal Allograft Stiffness and Viscosity Using 2D SWE PLUS and Vi PLUS Measures-A Pilot Study
- PMID: 35955985
- PMCID: PMC9369292
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm11154370
Assessment of Renal Allograft Stiffness and Viscosity Using 2D SWE PLUS and Vi PLUS Measures-A Pilot Study
Abstract
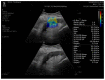
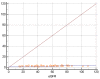
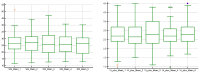
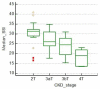
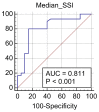
Elastography is a useful noninvasive tool for the assessment of renal transplant recipients. 2D-shear wave elastography (SWE) PLUS and viscosity plane-wave ultrasound (Vi PLUS) have emerged as novel techniques that promise to offer improved renal stiffness and viscosity measures due to improved processing algorithms. Methods: We performed a cross-sectional study of 50 kidney transplanted patients (16 women, 34 men; mean age of 47.5 ± 12.5; mean estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) estimated by Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration formula: 52.19 ± 22.6 mL/min/1.73 m2; and a mean duration after transplant of 10.09 ± 5 years). For every patient, we obtained five valid measurements of renal stiffness (obtained from five different frames in the cortex of the renal graft), and also tissue viscosity, with a C6-1X convex transducer using the Ultra-Fast™ software available on the Aixplorer Mach 30 ultrasound system (Supersonic Imagine, Aix-en-Provence, France). The median values of elastographic and viscosity measures have been correlated with the patients’ demographic, biological, and clinical parameters. Results: We obtained a cut-off value of renal cortical stiffness of <27.3 kiloPascal(kPa) for detection of eGFR < 60 mL/min/1.73 m2 with 80% sensitivity and 85% specificity (AUC = 0.811, p < 0.0001), a cut-off value of <26.9 kPa for detection of eGFR < 45 mL/min/1.73 m2 with 82.6% sensitivity and 74% specificity (AUC = 0.789, p < 0.0001), and a cut-off value of <23 kPa for detection of eGFR < 30 mL/min/1.73 m2 with 88.8% sensitivity and 75.6% specificity (AUC = 0.852, p < 0.0001). We found a positive correlation coefficient between eGFR and the median measure of renal cortical stiffness (r = 0.5699, p < 0.0001), between eGFR the median measure of viscosity (r = 0.3335, p = 0.0180), between median depth of measures and renal cortical stiffness (r = −0.2795, p = 0.0493), and between median depth of measures and body mass index (BMI) (r = 0.6574, p < 0.0001). Our study showed good intra-operator agreement for both 2D SWE PLUS measures—with an intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) of 0.9548 and a 95% CI of 0.9315 to 0.9719—and Vi PLUS, with an ICC of 0.8323 and a 95% CI of 0.7457 to 0.8959. The multivariate regression model showed that 2D SWE PLUS values were associated with eGFR, Vi PLUS, and depth of measures. Conclusions: Assessment of renal allograft stiffness and viscosity may prove to be an effective method for identifying patients with chronic allograft injury and could prove to be a low-cost approach to provide additional diagnostic information of kidney transplanted patients.
Keywords: 2D SWE PLUS; Vi PLUS; chronic kidney disease; stiffness; viscosity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Assessment of Thyroid Stiffness and Viscosity in Autoimmune Thyroiditis Using Novel Ultrasound-Based Techniques.Biomedicines. 2023 Mar 17;11(3):938. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11030938. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 36979917 Free PMC article.
-
Non-Invasive Evaluation of Kidney Elasticity and Viscosity in a Healthy Cohort.Biomedicines. 2022 Nov 8;10(11):2859. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10112859. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36359379 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship between Novel Elastography Techniques and Renal Fibrosis-Preliminary Experience in Patients with Chronic Glomerulonephritis.Biomedicines. 2023 Jan 26;11(2):365. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11020365. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 36830901 Free PMC article.
-
Agreement Between 2-Dimensional Shear Wave and Transient Elastography Values for Diagnosis of Advanced Chronic Liver Disease.Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020 Dec;18(13):2971-2979.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2020.04.034. Epub 2020 Apr 26. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020. PMID: 32348907
-
Diagnostic Accuracy Evaluation of Two-Dimensional Shear Wave Elastography in the Differentiation Between Benign and Malignant Thyroid Nodules: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.J Ultrasound Med. 2020 Sep;39(9):1729-1741. doi: 10.1002/jum.15271. Epub 2020 Mar 30. J Ultrasound Med. 2020. PMID: 32227500
Cited by
-
Evaluation of Robustness of S-Transform Based Phase Velocity Estimation in Viscoelastic Phantoms and Renal Transplants.IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2024 Mar;71(3):954-966. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2023.3323983. Epub 2024 Feb 26. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2024. PMID: 37824308 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of Thyroid Stiffness and Viscosity in Autoimmune Thyroiditis Using Novel Ultrasound-Based Techniques.Biomedicines. 2023 Mar 17;11(3):938. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11030938. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 36979917 Free PMC article.
-
Kidney cortex shear wave motion simulations based on segmented biopsy histology.Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2024 Mar;245:108035. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2024.108035. Epub 2024 Jan 15. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2024. PMID: 38290290 Free PMC article.
-
Non-Invasive Evaluation of Kidney Elasticity and Viscosity in a Healthy Cohort.Biomedicines. 2022 Nov 8;10(11):2859. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10112859. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36359379 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasound viscoelastic imaging in the noninvasive quantitative assessment of chronic kidney disease.Ren Fail. 2024 Dec;46(2):2407882. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2024.2407882. Epub 2024 Sep 30. Ren Fail. 2024. PMID: 39344493 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hu Q., Zhang W.-J., Lin Z.-Q., Wang X.-Y., Zheng H.-Y., Wei H.-M., He H.-G. Combined acoustic radiation force impulse and conventional ultrasound in the quantitative assessment of immunoglobulin a nephropathy. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2019;45:2309–2316. doi: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2019.05.013. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Săftoiu A., Gilja O.H., Sidhu P.S., Dietrich C.F., Cantisani V., Amy D., Bachmann-Nielsen M., Bob F., Bojunga J., Brock M., et al. The EFSUMB guidelines and recommendations for the clinical practice of elastography in non-hepatic applications: Update 2018. Ultraschall Med. 2019;40:425–453. doi: 10.1055/a-0838-9937. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bende F., Sporea I., Șirli R., Bâldea V., Lazăr A., Lupușoru R., Fofiu R., Popescu A. Ultrasound-Guided Attenuation Parameter (UGAP) for the quantification of liver steatosis using the Controlled Attenuation Parameter (CAP) as the reference method. Med. Ultrason. 2021;23:7–14. doi: 10.11152/mu-2688. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

