Anti-Hypertensive Activity of Some Selected Unani Formulations: An Evidence-Based Approach for Verification of Traditional Unani Claims Using LC-MS/MS for the Evaluation of Clinically Relevant Blood Parameters in Laboratory Rats
- PMID: 35956245
- PMCID: PMC9369749
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm11154628
Anti-Hypertensive Activity of Some Selected Unani Formulations: An Evidence-Based Approach for Verification of Traditional Unani Claims Using LC-MS/MS for the Evaluation of Clinically Relevant Blood Parameters in Laboratory Rats
Abstract
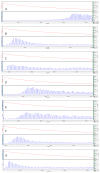
Background: Systemic arterial hypertension, which is associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease(CVD), is the most significant modifiable risk factor for mortality and morbidity worldwide. WHO has recognized Unanipathy as an alternate system of medicine. The aim of the present study is to investigate the anti-hypertensive activity of some selected unani formulations using L-NAME model. Method: Group I or hypertensive control group: L-NAME administered for 7 days and left for the next 7 days; Group II or KASgroup: L-NAME administered (i.p) for 7 days and L-NAME + KAS (1000 mg/kg b.w) for the next 7 days; Group III or DMM group: L-NAME administered (i.p) for 7 days and L-NAME + DMM (2000 mg/kg b.w) for the next 7 days; Group IV or MSR group: L-NAME administered (i.p) for 7 days and L-NAME + MSR (300 mg/kg b.w) for the next 7 days; Group V or HJ group: L-NAME administered (i.p) for 7 days and L-NAME + HJ (113 mg/kg b.w) for the next 7 days; Group VI or KGS group: L-NAME administered (i.p) for 7 days and L-NAME +KGS (2000 mg/kg b.w) for the next 7 days. Non-invasive systolic blood pressure and RR-interval (ECG) was measured. Plasma was investigated forsodium, potassium, nitrite, ANP, adrenaline, noradrenaline and aldosterone on day 0, 7 and 14 using LC-MS/MS. Result: Treatment showed a non-significant lowreduction in SBP (systolic blood pressure) of KAS, MSR and HJ while that of DMM was quite significant (p < 0.05), but in the case of KGS, SBP increased. DMM on day 14 significantly (p < 0.05) reduced plasma nitrite while no significant plasma Na+ was noted. In the case of both DMM and KGS, potassium increased significantly (p < 0.05) on day 14. No significant changes in plasma ANP and aldosterone was observed against DMM and KGS while blood levels of adrenaline and noradrenaline significantly (p < 0.05) changed. No significant change in body weight was found. Conclusions: L-NAME KAS, MSR and HJ showed no change in SBP while DMM showed a significant reduction in SBP with decreased plasma nitrite. Probably, DMM may have anti-hypertensive activity mediated through NO inhibition while KGS may involve central sympathomimetic action.
Keywords: ECG; adrenaline; noradrenaline; systolic blood pressure; unani system.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures







References
-
- Ministry of Health and Family Affairs . National Formulary of Unani Medicine (NFUM) Central Council for Research in Unani Medicine, Government of India, Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Department of Health; New Delhi, India: 2006. Part V; pp. 76, 79, 110.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

