Alleviating Effects of Black Soybean Peptide on Oxidative Stress Injury Induced by Lead in PC12 Cells via Keap1/Nrf2/TXNIP Signaling Pathway
- PMID: 35956280
- PMCID: PMC9370349
- DOI: 10.3390/nu14153102
Alleviating Effects of Black Soybean Peptide on Oxidative Stress Injury Induced by Lead in PC12 Cells via Keap1/Nrf2/TXNIP Signaling Pathway
Abstract
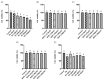
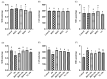
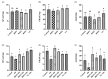
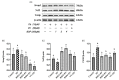
Many researchers have found that Pb exposure can cause oxidative stress damage to the body’s tissue. Black soybean peptide (BSP) has a variety of physiological functions, especially in terms of oxidative stress. Nevertheless, the mitigation function of BSPs on Pb-induced oxidative stress damage in PC12 cells has not been clearly defined. In this study, cell viability was detected by CCK8. Oxidative stress indicators, such as ROS, GSH/GSSG, MDA, SOD, CAT, GPx, and GR, were tested with biochemical kit. Protein expression of Keap1, Nrf2, and TXNIP was measured by Western blot. Compared with the control group, Pb reduced the cell viability of PC12 cells. However, BSP treatment significantly increased the viability of PC12 cells induced by lead exposure (p < 0.05). Lead can enrich the contents of MDA and ROS, but decrease the amount of CAT, SOD, GR, GPx, and GSH/GSSG in PC12 cells, while BSP can alleviate it (p < 0.05). Lead can enhance the expression of Keap1 and TXNIP proteins, but reduce Nrf2 expression. In contrast, BSPs reversed this phenomenon (p < 0.05). BSPs can alleviate oxidative stress injury induced by lead in PC12 cells through the Keap1/Nrf2/TXNIP signaling pathway.
Keywords: Keap1/Nrf2/TXNIP; PC12 cells; Pb; black soybean peptide; oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 202300410193/the Excellent Youth Project of the Natural Science Foundation of Henan Province
- NNSFC-31201878, U1204804, U1604183 and 32101966/the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2021GGJS035/the young backbone teacher of Henan Province
- 20171215/Henan Engineering Technology Research Center of Food Processing and Circulation Safety Control
- YJS2022JD16/Henan Province Postgraduate Joint Training Base Project
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

