Dietary Intake of Vegan and Non-Vegan Endurance Runners-Results from the NURMI Study (Step 2)
- PMID: 35956327
- PMCID: PMC9370654
- DOI: 10.3390/nu14153151
Dietary Intake of Vegan and Non-Vegan Endurance Runners-Results from the NURMI Study (Step 2)
Abstract
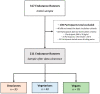
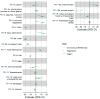
Nowadays, the growing popularity of distance running has been accompanied by the increasing prevalence of vegan and vegetarian diets, especially among endurance athletes. The present study aimed to examine the association between diet type and dietary intake of distance runners competing at distances longer than 10 km. From a total of 317 participants, 211 endurance runners (57% females) were considered the final sample after applying the exclusion criteria. Runners were assigned to three groups based on the self-reported diet types: 95 omnivores, 40 vegetarians, and 76 vegans. Data collection was conducted using an online survey with questions about sociodemographic information, dietary intake, and dietary-associated motives. A comprehensive food frequency questionnaire with 53 food groups (categorized in 14 basic-plus three umbrella-food clusters) was used to assess dietary intake. Vegan runners had a higher intake of "beans and seeds", "fruit and vegetables", and "dairy alternatives", as well as lower intakes of "oils" than other two groups. Vegetarian runners had a lower intake of "dairy products" and "eggs" than omnivores. A greater intake of "alcohol" and a lower intake of "meat alternatives" was observed in omnivorous runners compared to vegans and vegetarians. Despite the existence of a tendency toward the consumption of health-related food clusters by vegan runners, further investigations are needed to verify the predominance of vegans in health-oriented dietary patterns.
Keywords: athletes; dietary assessment; dietary patterns; endurance running; food frequency; health; lifestyle; marathon; nutrition; plant-based diet.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Supplement Intake in Recreational Vegan, Vegetarian, and Omnivorous Endurance Runners-Results from the NURMI Study (Step 2).Nutrients. 2021 Aug 10;13(8):2741. doi: 10.3390/nu13082741. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 34444901 Free PMC article.
-
Training and Racing Behaviors of Omnivorous, Vegetarian, and Vegan Endurance Runners-Results from the NURMI Study (Step 1).Nutrients. 2021 Oct 7;13(10):3521. doi: 10.3390/nu13103521. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 34684522 Free PMC article.
-
Female Endurance Runners Have a Healthier Diet than Males-Results from the NURMI Study (Step 2).Nutrients. 2022 Jun 22;14(13):2590. doi: 10.3390/nu14132590. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 35807768 Free PMC article.
-
Calcium intake in vegan and vegetarian diets: A systematic review and Meta-analysis.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2023;63(31):10659-10677. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2022.2084027. Epub 2022 Jun 6. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2023. PMID: 38054787
-
Vegans, Vegetarians, and Omnivores: How Does Dietary Choice Influence Iodine Intake? A Systematic Review.Nutrients. 2020 May 29;12(6):1606. doi: 10.3390/nu12061606. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32486114 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Completely Plant-Based Diets That Meet Energy Requirements for Resistance Training Can Supply Enough Protein and Leucine to Maximize Hypertrophy and Strength in Male Bodybuilders: A Modeling Study.Nutrients. 2024 Apr 10;16(8):1122. doi: 10.3390/nu16081122. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38674813 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of an 8-Week Vegan Diet on the Nutritional Status and Performance of Semi-Professional Soccer Players-Results of the VegInSoc Study.Nutrients. 2025 Jul 17;17(14):2351. doi: 10.3390/nu17142351. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 40732976 Free PMC article.
-
Racing Experiences of Recreational Distance Runners following Omnivorous, Vegetarian, and Vegan Diets (Part B)-Results from the NURMI Study (Step 2).Nutrients. 2023 May 9;15(10):2243. doi: 10.3390/nu15102243. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37242128 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary Antioxidants, Quality of Nutrition and Cardiovascular Characteristics among Omnivores, Flexitarians and Vegetarians in Poland-The Results of Multicenter National Representative Survey WOBASZ.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Jan 18;12(2):222. doi: 10.3390/antiox12020222. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36829779 Free PMC article.
-
Training Behaviors and Periodization Outline of Omnivorous, Vegetarian, and Vegan Recreational Runners (Part A)-Results from the NURMI Study (Step 2).Nutrients. 2023 Apr 6;15(7):1796. doi: 10.3390/nu15071796. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37049635 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wirnitzer K.C. Vegan diet in sports and exercise–health benefits and advantages to athletes and physically active people: A narrative review. Int. J. Sports Exerc. Med. 2020;6:165.
-
- Craig W.J., Mangels A.R. American Dietetic Association. Position of the American Dietetic Association: Vegetarian diets. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2009;109:1266–1282. - PubMed
-
- Eker S., Garcia D., Valin H., Ruijven B. Using social media audience data to analyse the drivers of low-carbon diets. Environ. Res. Lett. 2021;16:074001. doi: 10.1088/1748-9326/abf770. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

